In the diverse tapestry of the English language, compound nouns stand as intricate linguistic structures that weave together different elements to form a cohesive entity. These nouns can concisely convey complex ideas and objects, providing efficiency and clarity in communication.
In this exploration, we’ll unravel the intricacies of compound nouns, delving into their definition, identification, types, and the various ways they can be formed.
What is a Compound Noun?
When a noun or another part of speech combines with another noun or any other part of speech to form a noun, it is termed a compound noun. This unique structure is characterized by the amalgamation of multiple words, allowing for the creation of rich and nuanced expressions.
Examples of compound nouns include “football,” “chicken fries,” “passer-by,” or “water tank.” Each of these combines distinct elements to encapsulate a specific concept or object.
Identifying Compound Nouns
Identifying compound nouns involves recognizing a noun made up of two or more different words. These words can be connected in various ways, such as through spaces, hyphens, or seamlessly joined together. Compound nouns can span various categories, encompassing everyday objects, expressions, and complex ideas.
There are 3 types of compound nouns.
1. Spaced or Open Compound Noun
In this type, the compound noun consists of separate words, creating a distinct space between them. This form allows for clear individual recognition of each element while working together to convey a singular idea.
Examples
- Dining Room
- Swimming Pool
- Tennis Court
- Ice Cream.
2. Hyphenated Compound Nouns
In this type, words within the compound noun are connected by hyphens, indicating a closer relationship between the components. The hyphenation serves to emphasize the unity of the elements.
Examples
- Six-Pack
- Sister-in-law
- Well-being
- X-ray
3. Closed or Solid Compound Nouns
In this type, the words forming the compound noun are seamlessly joined together without spaces or hyphens. This results in a single, cohesive term that often represents a specific object, place, or concept.
Examples
- Bedroom
- Notebook
- Bookstore
- Toothpaste
Forming Compound Nouns
Compound nouns involve skillful combinations of words, resulting in unique and cohesive terms that efficiently convey specific meanings. Let’s explore the various ways compound nouns can be formed and understand the nuances of each construction.
1. Noun + Noun
Example: air pollution, car park
Explanation: This formation involves two nouns placed together, where the first Noun modifies or describes the second one. In “air pollution,” the air is modified by the type of pollution, and in “car park,” the park is specified as a place for cars.
2. Noun + Verb
Example: sunrise, rainfall
Explanation: Here, a noun is combined with a verb, often expressing an action or a natural phenomenon. In “sunrise,” the Noun (sun) is associated with the action of rising, and in “rainfall,” the Noun (rain) is connected with the action of falling.
3. Noun + Gerund
Example: swimming pool, dancing shoes
Explanation: This construction involves a noun paired with a gerund, forming compound nouns that represent an activity or object related to the Gerund. In “swimming pool,” the pool is designated for swimming, and in “dancing shoes,” the shoes are meant for dancing.
4. Gerund + Noun
Example: running shoes, writing desk
Explanation: The order is reversed here, with the Gerund preceding the Noun. In “running shoes,” the shoes are designed for running, and in “writing desk,” the desk is used for writing.
5. Noun + Preposition + Noun
Example: daughter-in-law, passer-by
Explanation: This structure includes a noun followed by a preposition and another noun, often denoting relationships or roles. In “daughter-in-law,” the relationship is specified, and in “passer-by,” the person is identified as someone passing by.
6. Preposition + Verb
Example: input, output
Explanation: Compound nouns can also be formed by combining a preposition with a verb, creating terms related to processes or actions. In “input,” the Preposition indicates the direction of the action, and in “output,” it signifies the result or outcome.
7. Verb + Preposition
Example: breakdown, set up
Explanation: In this construction, a verb is paired with a preposition to form compound nouns reflecting actions or processes. “Breakdown” refers to the process of breaking down, and “set up” indicates the arrangement or establishment of something.
8. Preposition + Noun
Example: underground, outdoors
Explanation: Compound nouns can arise from combining a preposition and a noun, often denoting locations or spaces. “Underground” refers to a location beneath the ground, and “outdoors” signifies an open-air space.
9. Adjective + Noun
Example: bluebird, darkroom
Explanation: When an adjective is coupled with a noun, it forms a compound noun expressing a specific quality or characteristic. In “bluebird,” the bird is characterized by its color, and in “darkroom,” the room is identified by its lighting conditions.
10. Adjective + Verb
Example: loudspeaker, high jump
Explanation: This construction combines an adjective with a verb to create compound nouns related to actions or qualities. In “loudspeaker,” the speaker is characterized by its volume, and in “high jump,” the jump is associated with its height.
11. Repetitive Words
Example: choo-choo (train), bye-bye
Explanation: Compound nouns with repetitive words often convey a sense of familiarity or playfulness. In “choo-choo,” the repetition mimics the sound of a train, and in “bye-bye,” the repetition emphasizes the act of saying goodbye.
12. Places
Example: airport, courthouse
Explanation: Compound nouns formed with place names indicate specific locations or establishments. In “airport,” it is a place for air travel, and in “courthouse,” it is a location where legal matters are addressed.
13. Nationalities
Example: Frenchman, Englishwoman
Explanation: Compound nouns can also denote individuals based on nationality. In “Frenchman,” the person is identified as being from France, and in “Englishwoman,” the individual is associated with England.
14. Titles
Example: dishwasher, postman
Explanation: Compound nouns can represent roles or job titles. In “dishwasher,” it refers to a machine or a person washing dishes, and in “postman,” it signifies an individual delivering mail.
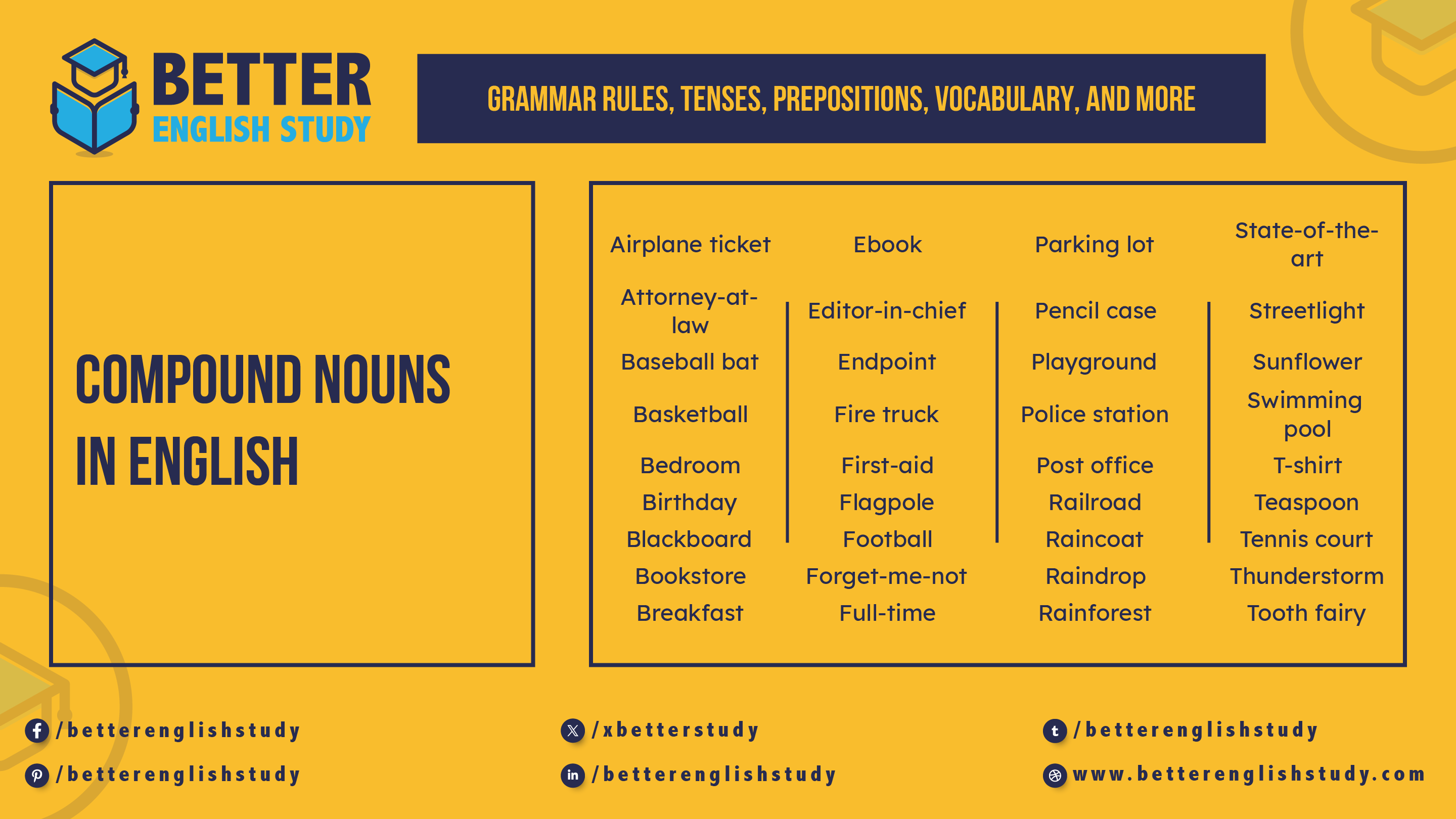
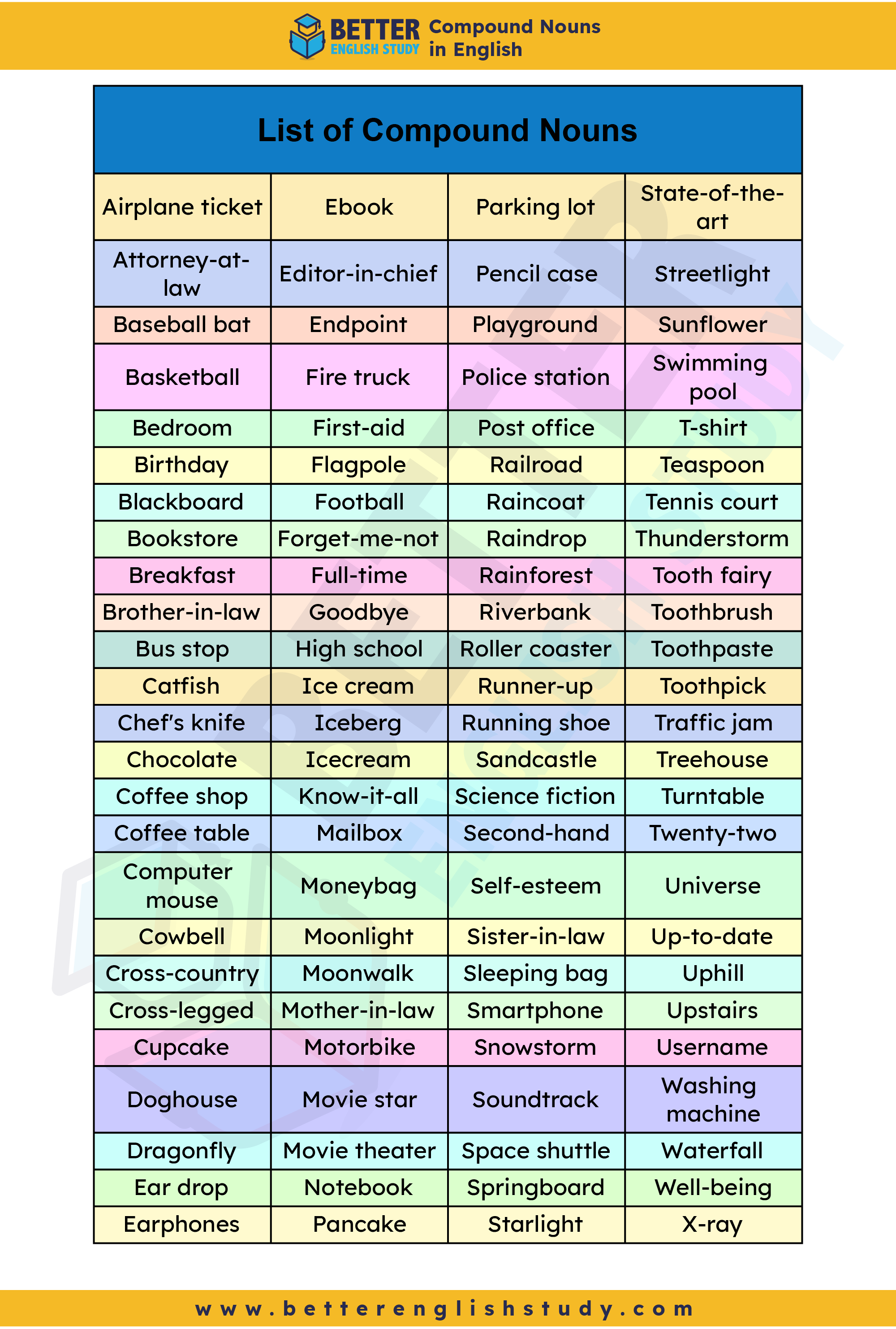
List of 100 Compound Nouns
| Airplane ticket | Ebook | Parking lot | State-of-the-art |
| Attorney-at-law | Editor-in-chief | Pencil case | Streetlight |
| Baseball bat | Endpoint | Playground | Sunflower |
| Basketball | Fire truck | Police station | Swimming pool |
| Bedroom | First-aid | Post office | T-shirt |
| Birthday | Flagpole | Railroad | Teaspoon |
| Blackboard | Football | Raincoat | Tennis court |
| Bookstore | Forget-me-not | Raindrop | Thunderstorm |
| Breakfast | Full-time | Rainforest | Tooth fairy |
| Brother-in-law | Goodbye | Riverbank | Toothbrush |
| Bus stop | High school | Roller coaster | Toothpaste |
| Catfish | Ice cream | Runner-up | Toothpick |
| Chef’s knife | Iceberg | Running shoe | Traffic jam |
| Chocolate | Icecream | Sandcastle | Treehouse |
| Coffee shop | Know-it-all | Science fiction | Turntable |
| Coffee table | Mailbox | Second-hand | Twenty-two |
| Computer mouse | Moneybag | Self-esteem | Universe |
| Cowbell | Moonlight | Sister-in-law | Up-to-date |
| Cross-country | Moonwalk | Sleeping bag | Uphill |
| Cross-legged | Mother-in-law | Smartphone | Upstairs |
| Cupcake | Motorbike | Snowstorm | Username |
| Doghouse | Movie star | Soundtrack | Washing machine |
| Dragonfly | Movie theater | Space shuttle | Waterfall |
| Ear drop | Notebook | Springboard | Well-being |
| Earphones | Pancake | Starlight | X-ray |
Examples of Compound Nouns in a Sentence
- Swimming Pool: The big swimming pool has clear water for splashing and playing.
“Swimming pool” is a compound noun combining the swimming activity with the container for water, forming a cohesive term for a specific recreational facility.
- Rainfall: The farmers eagerly awaited the forecasted heavy rainfall to nourish their crops.
“Rainfall” is a compound noun representing the action of rain falling, expressing the quantity of precipitation over a specific area.
- Bedroom: My sister loves to decorate her cozy bedroom with comfortable furniture.
“Bedroom” is a compound noun merging the idea of a bed with a room, creating a dedicated space for rest.
- Dishwasher: The modern kitchen has a high-tech dishwasher that cleans and dries dishes efficiently.
“Dishwasher” combines the function of washing dishes with the device itself, streamlining the term for a kitchen appliance.
- Bluebird: Look at the pretty bluebird! It has bright blue feathers and loves to sing.
“Bluebird” fuses the characteristic color with the type of bird, forming a compound noun that vividly describes a specific avian species.
- Well-being: Regular exercise and a balanced diet are essential for overall well-being.
“Well-being” combines the state of being well with the encompassing concept of health and happiness.
- Sister-in-law: My sister-in-law is a talented artist who creates beautiful paintings.
“Sister-in-law” merges the familial connection of a sister with the marital relationship, creating a compound noun for a sibling by marriage.
- Sunrise: The beautiful sunrise colors the sky pink and orange every morning.
“Sunrise” combines the celestial body (sun) with the action of rising, capturing the beauty of the morning phenomenon.
- Air Pollution: Reducing air pollution is crucial for ensuring a cleaner and healthier environment.
“Air pollution” blends the element of air with undesirable pollution quality, highlighting a specific environmental issue.
- Frenchman: The chef, a talented Frenchman, makes delicious food from France.
“Frenchman” combines the nationality (French) with the individual, creating a compound noun that specifies a person from France.
The compound noun enhances precision and clarity in each example by combining distinct elements to form a cohesive term. These combinations efficiently convey specific ideas, objects, or relationships in English.
In conclusion, compound nouns are a fascinating and expansive realm within English grammar. These linguistic formations showcase the language’s adaptability and richness, allowing for the encapsulation of complex ideas in succinct and efficient expressions. So, the next time you encounter a compound noun, take a moment to appreciate the creativity and precision woven into its composition.
