Imagine you’re telling a story about your friend Sahil. Instead of repeating his name over and over, you can say “he” or “him.” This is where pronouns come in handy. Pronouns make our language flow smoothly and help avoid repetitive sentences.
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of pronouns, exploring their types and providing clear examples to help you understand how to use them effectively.
What Are Pronouns in English?
A pronoun is a word used to replace a noun. Pronouns are words (or phrases) you substitute for nouns when the reader already knows which noun is being referred to. For instance, instead of saying, “Maria went to Maria’s car,” you can say, “Maria went to her car.”
Pronouns can be used in singular and plural forms, making them essential tools in both written and spoken English.
Definition of Pronouns
According to Merriam-Webster, a pronoun is “any of a small set of words in a language that are used as substitutes for nouns or noun phrases and whose referents are named or understood in the context.”
The Cambridge Dictionary defines a pronoun as “a word that is used instead of a noun or a noun phrase.”
According to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionaries, a pronoun is “a word that is used in place of a noun or noun phrase.”
Types of Pronouns with Examples
Pronouns Classified by Person and Number
Pronouns are generally classified into three main kinds based on person and number: first person, second person, and third person. Each kind has singular and plural forms.
| Person | Singular Pronoun | Plural Pronoun |
| First Person Pronoun | I, Me | We, Us |
| Second Person Pronoun | You, Your | You |
| Third Person Pronoun | He, She, It, Him, Her | They, Them, Their |
Examples
- First Person Pronouns
- Singular: I am going to the store. / This book is for me.
- Plural: We are planning a trip. / The teacher gave us homework.
- Second Person Pronouns
- Singular: You need to finish your work. / Is this book yours?
- Plural: You all need to submit your assignments by Friday.
- Third Person Pronouns
- Singular: He is my friend. / She loves to read. / It is raining outside.
- Him, Her: I saw him at the park. / Give the book to her.
- Plural: They are going to the concert. / The gift is for them. / Their house is on the corner.
- Singular: He is my friend. / She loves to read. / It is raining outside.
Pronouns also can be classified into different types based on their functions. Let, ‘s explore those various types of pronouns with examples below.
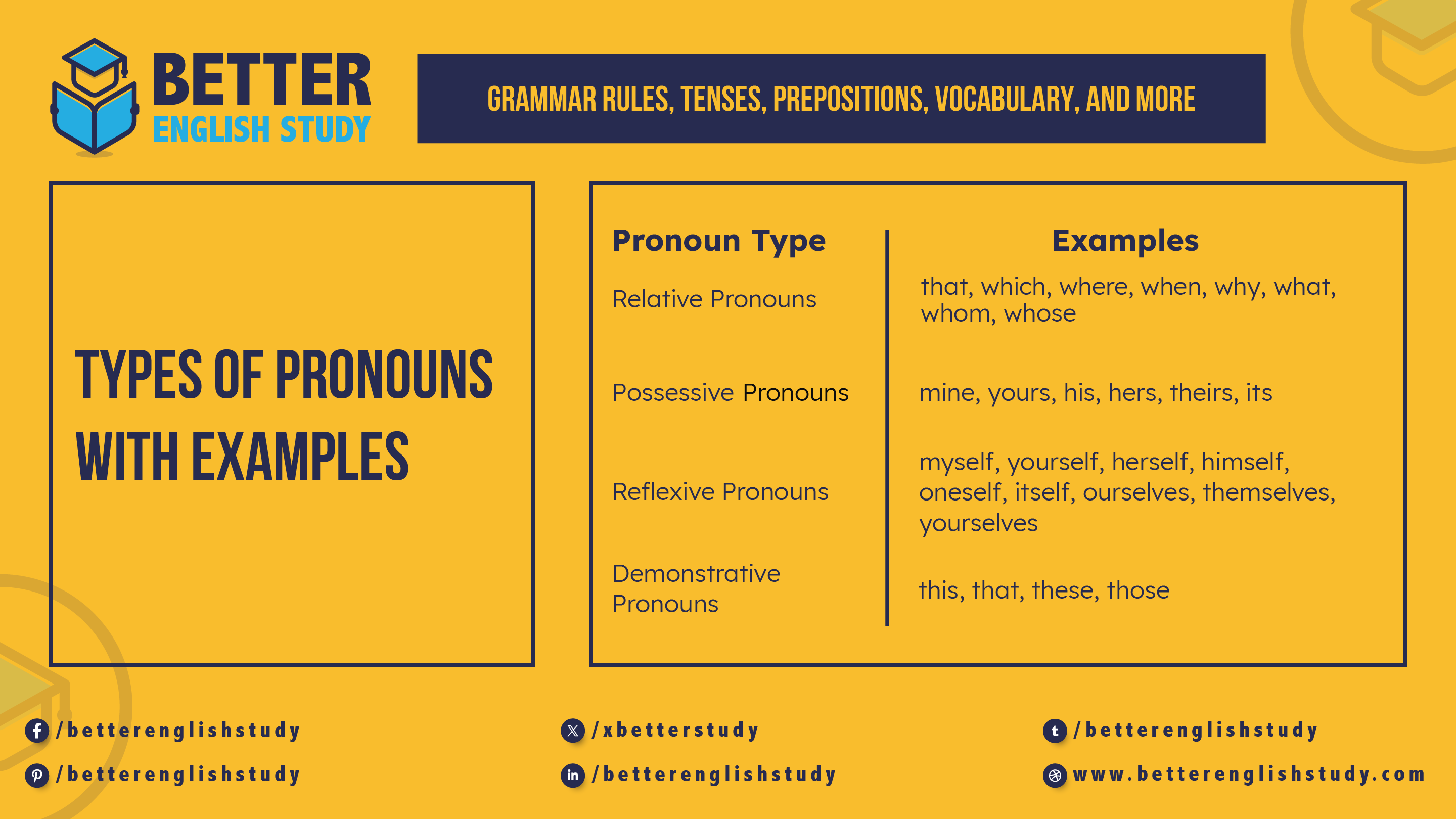
1. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are used to link clauses to a noun or a pronoun. They provide more information about the noun they refer to. Some common relative pronouns are: that, which, where, when, why, what, whom, and whose.
- The book that you gave me is fascinating.
- She lives in the house where she grew up.
- Do you remember the time when we first met?
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns show ownership or possession. They help indicate that something belongs to someone or something. Examples include mine, yours, his, hers, theirs, its.
- This pen is mine.
- The decision is yours to make.
- The responsibility was theirs.
3. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same person or thing. Examples include myself, yourself, herself, himself, oneself, itself, ourselves, themselves, and yourselves.
- I taught myself to play the guitar.
- She prepared the meal herself.
- The cat cleaned itself.
4. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific things. These pronouns are: this, that, these, those.
- This is my favorite book.
- Those were the best days of my life.
- These cookies are delicious.
5. Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. They include: who, what, when, why, where.
- Who is coming to the party?
- What is your name?
- Where do you live?
6. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people or things. Examples include someone, somebody, somewhere, something, anyone, anybody, anywhere, anything, no one, nobody, nowhere, everyone, everybody, everywhere, everything, each, none, few, many.
- Someone left their bag here.
- Everybody is welcome to join.
- Many were called, but few were chosen.
7. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things. They are divided into subject and object pronouns. Examples include: I, you, he, she, we, they, him, her, it, us, them.
- I am going to the market.
- She loves to read books.
- Can you help them?
8. Subject Pronouns
Subject pronouns are used as the subject of a sentence. They include I, you, we, he, she, it, they, one.
- We are going to the beach.
- He is my brother.
- One must be careful while driving.
9. Object Pronouns
Object pronouns are used as the object of a verb or a preposition. Examples include me, us, him, her, them.
- She called me yesterday.
- The teacher gave us homework.
- They saw her at the store.
10. Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns are used to indicate a mutual action or relationship. They include each other, one another.
- The friends helped each other with their homework.
- The team members respect one another.
11. Intensive Pronouns
Intensive pronouns emphasize a preceding noun or pronoun. They look the same as reflexive pronouns but are used differently. Examples include: myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
- The CEO herself attended the meeting.
- The children made the cake themselves.
- I will handle this project myself.
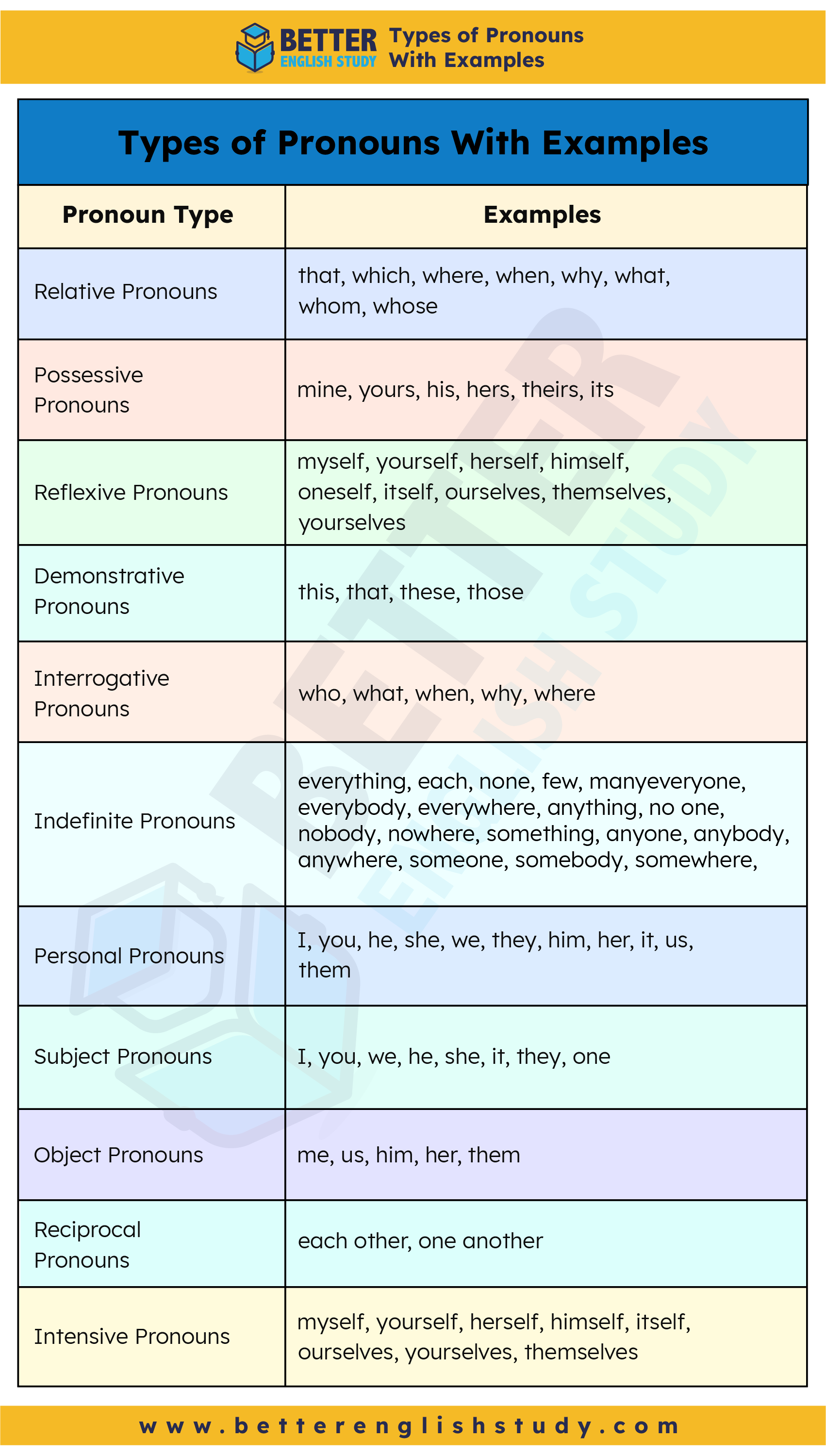
Types of Pronouns With Examples
| Pronoun Type | Examples |
| Relative Pronouns | that, which, where, when, why, what, whom, whose |
| Possessive Pronouns | mine, yours, his, hers, theirs, its |
| Reflexive Pronouns | myself, yourself, herself, himself, oneself, itself, ourselves, themselves, yourselves |
| Demonstrative Pronouns | this, that, these, those |
| Interrogative Pronouns | who, what, when, why, where |
| Indefinite Pronouns | someone, somebody, somewhere, something, anyone, anybody, anywhere, anything, no one, nobody, nowhere, everyone, everybody, everywhere, everything, each, none, few, many |
| Personal Pronouns | I, you, he, she, we, they, him, her, it, us, them |
| Subject Pronouns | I, you, we, he, she, it, they, one |
| Object Pronouns | me, us, him, her, them |
| Reciprocal Pronouns | each other, one another |
| Intensive Pronouns | myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves |
Pronouns are an essential part of English grammar, and they are used every day to make sentences clear and concise. Whether referring to people, places, things, or ideas, pronouns help us communicate effectively by avoiding redundancy. By understanding and using the various types of pronouns correctly, you can improve both your written and spoken English.
