Have you ever found yourself comparing two things, trying to decide which is better, faster, or more interesting? Comparative adjectives are the tools we use to compare differences between the two objects they modify.
Understanding how to use them can greatly enhance your ability to express comparisons in English, making your descriptions more precise and engaging.
What Are Comparative Adjectives?
Comparative adjectives are used to compare one person or thing with another and enable us to say whether a person or thing has more or less of a particular quality. They help us highlight differences and make our language more vivid and descriptive.
For example:
- This car is faster than that one.
- She is taller than her brother.
These adjectives usually end in “-er” or are preceded by “more” or “less.”
Definition of Comparative Adjectives
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, a comparative adjective is defined as “an adjective that is used to show the difference between two objects by comparing them” (source: Cambridge Dictionary).
How to Use Comparative Adjectives in a Sentence
Using comparative adjectives correctly involves understanding the structure of the sentence and the specific adjective’s form. Comparative adjectives are typically used in a specific sentence structure that allows for a clear comparison between two entities.
Here is a formula that can help you construct sentences with comparative adjectives:
Subject + Verb + Comparative Adjective + than + Object
Examples:
1. John is stronger than Mike.
- Subject: John
- Verb: is
- Comparative Adjective: stronger
- Object: Mike
- Explanation: The comparative adjective “stronger” modifies the noun “John” and compares his strength to Mike’s.
2. This puzzle is easier than the last one.
- Subject: This puzzle
- Verb: is
- Comparative Adjective: easier
- Object: the last one
- Explanation: The comparative adjective “easier” modifies the noun “this puzzle” and compares its difficulty to the last puzzle.
3. She is more intelligent than her peers.
- Subject: She
- Verb: is
- Comparative Adjective: more intelligent
- Object: her peers
- Explanation: The comparative adjective “more intelligent” modifies the noun “she” and compares her intelligence to that of her peers.
Let’s break down some more sentences to understand how comparative adjectives work:
4. My car is faster than yours.
- Subject: My car
- Verb: is
- Comparative Adjective: faster
- Object: yours
- Explanation: “Faster” compares the speed of “my car” with “your car.”
5. This book is more interesting than that one.
- Subject: This book
- Verb: is
- Comparative Adjective: more interesting
- Object: that one
- Explanation: “More interesting” compares the level of interest between “this book” and “that book.”
In each example, the comparative adjective modifies the noun and provides a clear comparison, making it easy to understand which entity possesses a greater or lesser degree of the quality described by the adjective.

Rules for Forming Comparative Adjectives
Forming comparative adjectives follows certain rules depending on the adjective’s length and ending. Here are the main rules:
1. One-Syllable Adjectives
For most one-syllable adjectives, add “-er.”
- Tall → Taller
- Fast → Faster
2. Adjectives Ending in -e
For adjectives ending in “-e,” add “-r.”
- Large → Larger
- Nice → Nicer
3. Adjectives Ending in a Consonant-Vowel-Consonant
For adjectives ending in a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern, double the final consonant and add “-er.”
- Big → Bigger
- Hot → Hotter
4. Two-syllable adjectives Ending in -y
For two-syllable adjectives ending in “-y,” change the “y” to “i” and add “-er.”
- Happy → Happier
- Busy → Busier
5. Adjectives with Two or More Syllables
For adjectives with two or more syllables, use “more” or “less” before the adjective.
- Beautiful → More beautiful
- Interesting → More interesting
Comparative Adjectives Table
| Regular Adjective | Comparative Adjective |
| Small | Smaller |
| Large | Larger |
| Fast | Faster |
| High | Higher |
| Easy | Easier |
| Busy | Busier |
| Happy | Happier |
| Strong | Stronger |
| Intelligent | More intelligent |
| Beautiful | More beautiful |
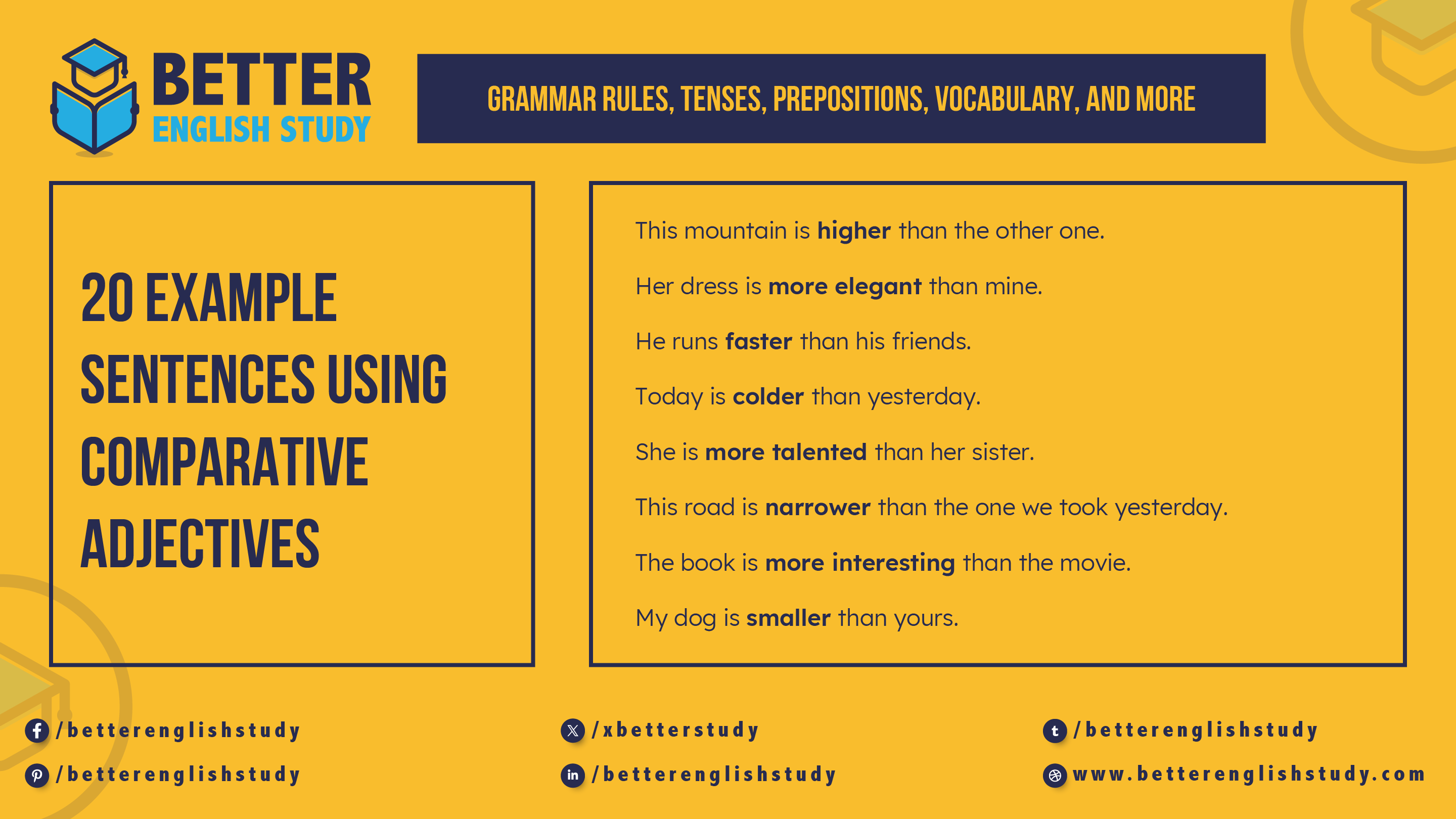
20 Example Sentences Using Comparative Adjectives
- This mountain is higher than the other one.
- Her dress is more elegant than mine.
- He runs faster than his friends.
- Today is colder than yesterday.
- She is more talented than her sister.
- This road is narrower than the one we took yesterday.
- The book is more interesting than the movie.
- My dog is smaller than yours.
- He is less experienced than his colleague.
- This chair is more comfortable than that one.
- The new model is cheaper than the old one.
- His house is larger than ours.
- The test was easier than we expected.
- Her smile is brighter than the sun.
- This solution is more effective than the previous one.
- He is quicker than his opponent.
- She sings better than anyone I know.
- This painting is more vibrant than the other one.
- The soup is hotter than it was before.
- He is taller than his father.
Comparative adjectives are essential for comparing differences between the two objects they modify. They allow us to articulate nuanced differences and enrich our communication. By understanding and practicing these rules and examples, you can enhance your English skills and describe the world around you with greater accuracy and detail.
