
Mastering English tenses can feel like a daunting task, especially if English isn’t your first language. You might find yourself wondering whether to say, “I work,” “I worked,” or “I will work.” Understanding when and how to use these different forms is essential for clear and effective communication.
This article will guide you through the rules of tenses, helping you to grasp their usage and avoid common mistakes.
Introduction to English Tenses
What Are Tenses in English Grammar?
Tenses are a fundamental part of English grammar. They indicate the time when an action occurs—whether in the present, past, or future. By changing the form of a verb, you can express when something happens, giving the context and clarity of your sentence.
Why Are Tenses Important in English?
Tenses allow us to communicate about different times in a clear and structured way. Imagine trying to tell a story about your past without using the correct tense—you might confuse your listener and fail to convey the sequence of events accurately.
Correct use of tenses ensures that your meaning is clear, whether you’re talking about daily habits, past experiences, or future plans.
How Many Tenses Are There in English?
In English, there are three main tenses: present, past, and future. Each of these tenses has four forms: simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. Together, they create a total of twelve tenses that help you express actions and states of being with precision.
1. Present Tense
What Is the Present Tense?
The present tense is used to describe actions that are currently happening, actions that happen regularly, or truths that are always valid. It’s like capturing a snapshot of the present moment.
Types of Present Tense
a) Present Simple
Rule: The present simple tense is formed by using the base form of the verb for all subjects except third-person singular, where you add an “-s” or “-es.”
Examples:
- She drives to work every day.
- They study English at night.
- The sun rises in the east.
- He teaches mathematics at the local school.
- We enjoy reading books on weekends.
b) Present Continuous
Rule: The present continuous tense is formed by using the verb “to be” (am/is/are) + the base form of the verb + “-ing.”
Examples:
- I am eating lunch right now.
- They are playing soccer in the park.
- She is working on her project at the moment.
- The children are watching a movie.
- He is studying for his exams this evening.
c) Present Perfect
Rule: The present perfect tense is formed by using the verb “to have” (have/has) + the past participle of the verb.
Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has traveled to Japan twice.
- They have lived in this city for five years.
- We have seen that movie before.
- He has written three books.
d) Present Perfect Continuous
Rule: The present perfect continuous tense is formed by using the verb “to have” (have/has) + been + the base form of the verb + “-ing.”
Examples:
- She has been reading the novel all day.
- They have been working on this project for weeks.
- I have been learning English for three years.
- He has been exercising regularly since January.
- We have been waiting for the bus for 30 minutes.
When and How to Use the Present Tense?
Use the present simple for regular actions and general truths, the present continuous for actions happening now, the present perfect for actions that have relevance to the present, and the present perfect continuous for actions that started in the past and are still ongoing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Present Tense
A common mistake is using the present simple when the present continuous is needed. For example, saying “I work now” instead of “I am working now” can lead to confusion about the timing of the action.
2. Past Tense
What Is the Past Tense?
The past tense is used to describe actions that have already happened. It allows you to talk about events that occurred at a specific time in the past.
Types of Past Tense
a) Past Simple
Rule: The past simple tense is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of regular verbs, while irregular verbs have unique past forms.
Examples:
- She visited her grandmother last weekend.
- They studied hard for the test.
- I went to the market yesterday.
- He saw a movie last night.
- We played football after school.
b) Past Continuous
Rule: The past continuous tense is formed by using the verb “to be” (was/were) + the base form of the verb + “-ing.”
Examples:
- I was reading a book when you called.
- They were playing chess at 5 PM.
- She was cooking dinner when the power went out.
- We were watching TV all evening.
- He was sleeping when the phone rang.
c) Past Perfect
Rule: The past perfect tense is formed by using the verb “to have” (had) + the past participle of the verb.
Examples:
- She had finished her homework before dinner.
- They had left the party by the time we arrived.
- I had seen the movie before it was released on DVD.
- He had already eaten when we invited him to dinner.
- We had visited Paris before our trip to Rome.
d) Past Perfect Continuous
Rule: The past perfect continuous tense is formed by using the verb “to have” (had) + been + the base form of the verb + “-ing.”
Examples:
- She had been studying for hours before the exam started.
- They had been working on the project all night.
- I had been waiting for the bus for 20 minutes before it arrived.
- He had been living in London before moving to New York.
- We had been talking for an hour before realizing the time.
When and How to Use the Past Tense?
Use the past simple for completed actions, the past continuous for actions that were in progress at a specific time, the past perfect for actions completed before another action, and the past perfect continuous for ongoing actions interrupted by another event.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Past Tense
A typical mistake is using the past simple when the past perfect is needed, like saying “I finished my work before he arrived” instead of “I had finished my work before he arrived.”
3. Future Tense
What Is the Future Tense?
The future tense is used to describe actions that will happen in the future. It allows you to talk about plans, predictions, and intentions.
Types of Future Tense
a) Future Simple
Rule: The future simple tense is formed by using “will” + the base form of the verb.
Examples:
- I will call you tomorrow.
- They will visit us next week.
- She will start her new job on Monday.
- We will go to the park later.
- He will arrive at 6 PM.
b) Future Continuous
Rule: The future continuous tense is formed by using “will be” + the base form of the verb + “-ing.”
Examples:
- I will be working at 8 PM tonight.
- They will be traveling to Paris this time tomorrow.
- She will be studying at the library in the afternoon.
- We will be having dinner at 7 PM.
- He will be sleeping when you arrive.
c) Future Perfect
Rule: The future perfect tense is formed by using “will have” + the past participle of the verb.
Examples:
- I will have finished my report by tomorrow morning.
- They will have left by the time you arrive.
- She will have completed the project by next week.
- We will have eaten dinner by 8 PM.
- He will have graduated by this time next year.
d) Future Perfect Continuous
Rule: The future perfect continuous tense is formed by using “will have been” + the base form of the verb + “-ing.”
Examples:
- I will have been working here for ten years next month.
- They will have been traveling for 24 hours by the time they reach home.
- She will have been studying for five hours by the time you arrive.
- We will have been living in this house for a decade by next year.
- He will have been running for two hours by the time the race ends.
When and How to Use the Future Tense?
Use the future simple for planned or predicted actions, the future continuous for actions that will be in progress at a specific time, the future perfect for actions that will be completed by a certain time, and the future perfect continuous for ongoing actions that will be happening up until a specific future point.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Future Tense
A common error is using the future simple when the future continuous is needed, like saying “I will eat dinner at 7 PM” instead of “I will be eating dinner at 7 PM.”
Mixed Tenses and Their Uses
How to Use Mixed Tenses in a Sentence?
In conversation, it’s common to use more than one tense within a sentence or paragraph to convey different time frames. For example, you might say, “I have been studying English for three years, and I will continue learning it until I’m fluent.”
Examples of Mixed Tenses in Conversation
- “I had finished my work before he arrived, and now I am resting.”
- “She has been working here for five years, but she will be moving to another city next month.”
- “They were playing football when it started raining, and they had to stop the game.”
- “By the time you get here, I will have completed the project, and we can celebrate.”
- “I have already eaten lunch, but I will join you for coffee.”
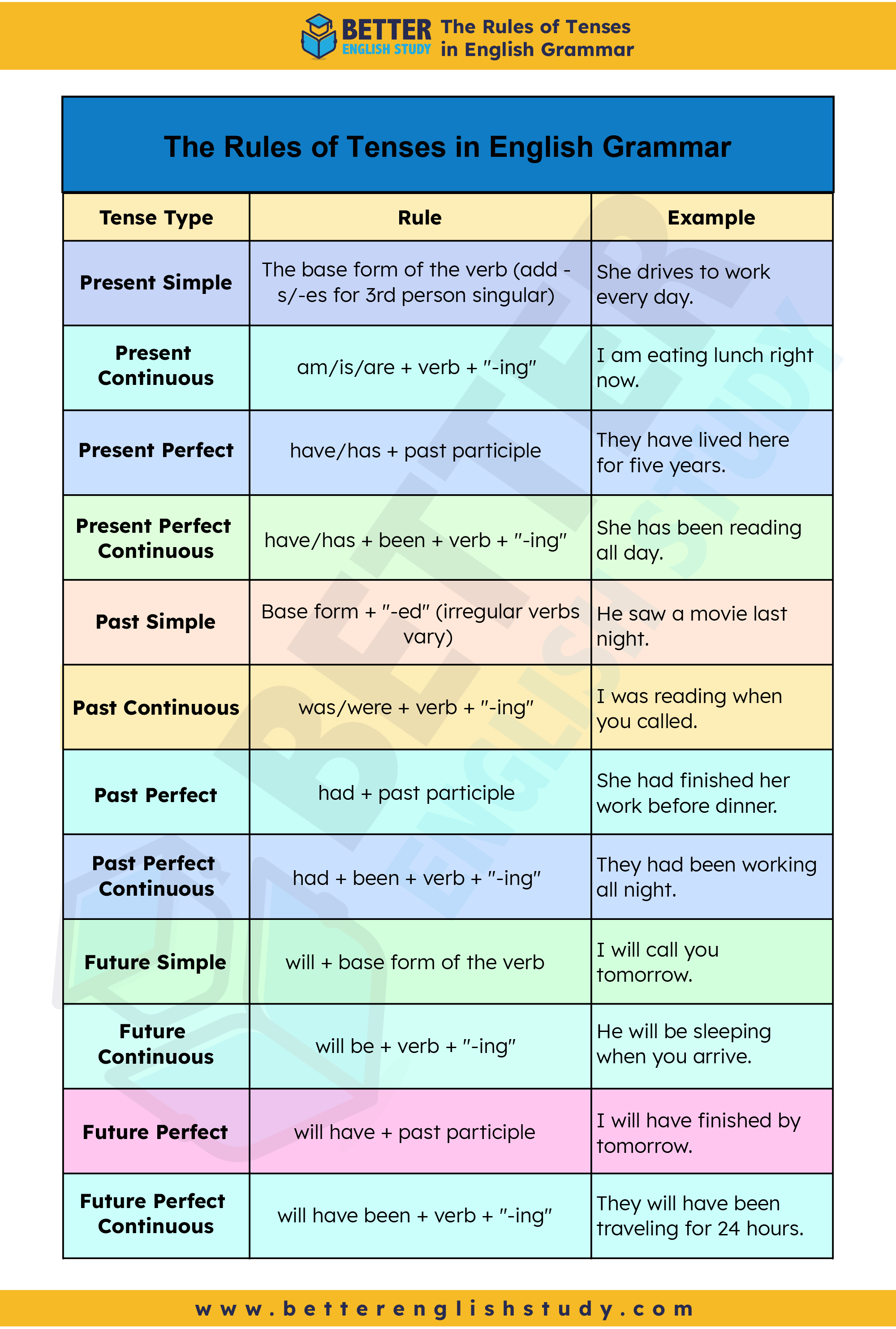
Summary Table of 12 Tenses Rules in English
| Tense Type | Rule | Example |
| Present Simple | The base form of the verb (add -s/-es for 3rd person singular) | She drives to work every day. |
| Present Continuous | am/is/are + verb + “-ing” | I am eating lunch right now. |
| Present Perfect | have/has + past participle | They have lived here for five years. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | have/has + been + verb + “-ing” | She has been reading all day. |
| Past Simple | Base form + “-ed” (irregular verbs vary) | He saw a movie last night. |
| Past Continuous | was/were + verb + “-ing” | I was reading when you called. |
| Past Perfect | had + past participle | She had finished her work before dinner. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | had + been + verb + “-ing” | They had been working all night. |
| Future Simple | will + base form of the verb | I will call you tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | will be + verb + “-ing” | He will be sleeping when you arrive. |
| Future Perfect | will have + past participle | I will have finished by tomorrow. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | will have been + verb + “-ing” | They will have been traveling for 24 hours. |
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Tenses are an essential part of English grammar, helping you to express actions in different time frames. The twelve tenses—present, past, and future in their simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms—allow for precise communication about when actions occur.
Tips for Mastering English Tenses
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice helps internalize the rules of tenses.
- Listen and Read: Engage with English media to see how tenses are used naturally.
- Seek Feedback: Don’t be afraid to ask others to correct your tense usage.
- Start Simple: Begin with the basics and gradually incorporate more complex tenses into your speech and writing.
With time and practice, understanding and using tenses will become second nature, allowing you to express yourself clearly and confidently in English.
