Embarking on mastering English can be an intriguing adventure for language learners. Amidst the various complexities, the distinction between ‘can’ and ‘could’ stands out as a crucial yet nuanced aspect.
These modal verbs, seemingly interchangeable, hold subtle differences that wield significant influence over the meaning of sentences.
In this exploration, we will unravel the mysteries surrounding ‘can’ and ‘could,’ providing clarity and concrete examples to guide learners through their proper usage.
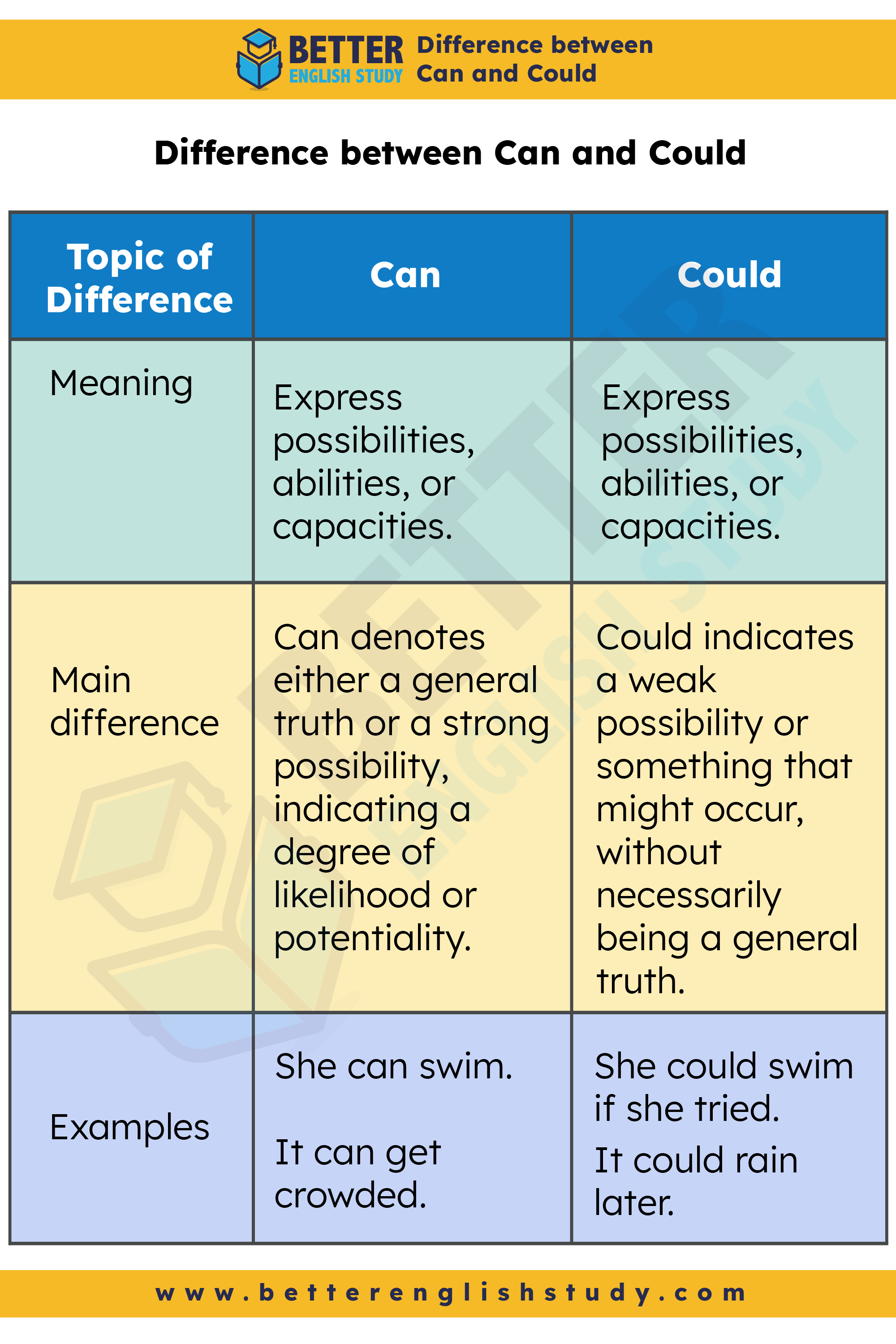
Difference between Can and Could
| Topic of Difference | Can | Could |
| Meaning | Express possibilities, abilities, or capacities. | Express possibilities, abilities, or capacities. |
| Main difference | Can denotes either a general truth or a strong possibility, indicating a degree of likelihood or potentiality. | Could indicates a weak possibility or something that might occur, without necessarily being a general truth. |
| Examples | She can swim. | She could swim if she tried. |
| It can get crowded. | It could rain later. |
Can or Could – When to Use
1. Present Ability or Possibility
- Can: She can speak Spanish fluently.
In this instance, ‘can’ is used to express her current ability to speak Spanish fluently.
- Could: She could join us for dinner tonight.
Here, ‘could’ suggests a potential event, indicating a weaker likelihood of her joining.
2. Politeness and Formality
- Can: Can I borrow your pen?
‘Can’ is suitable for informal settings when seeking permission for everyday actions.
- Could: Could I have a moment of your time?
‘Could’ is employed in more formal contexts, especially when making polite requests.
3. Future Possibility
- Can: The team can win the championship.
In this case, ‘can’ asserts a strong possibility of winning future competitions.
- Could: They could win if they play strategically.
‘Could’ implies a potential victory but with a less specific assurance.
Should I Use Can I or Could I?
When crafting questions, the choice between ‘can’ and ‘could’ depends on formality and context:
- Can I: Can I use your phone?
Use ‘can’ in casual or everyday situations to seek permission.
- Could I: Could I have a moment of your time?
Opt for ‘could’ in more formal or polite settings when making requests.
Which is More Formal: Can or Could?
‘Could’ is generally considered more formal than ‘can.’ Thus, choosing ‘could’ is often more appropriate in formal or polite contexts.
Examples
- Can: Can I have a piece of cake?
In casual situations, such as among friends or family, ‘can’ is acceptable for seeking permission.
- Could: Could I have a piece of cake, please?
However, when the context demands a touch of formality or politeness, ‘could’ adds a courteous tone, making the request more refined.
Can We Use Could for Future?
Yes, ‘could’ can be used to express future possibilities, especially when the likelihood is uncertain or contingent on specific conditions.
Examples
- The team could win the championship if they play strategically.
Here, ‘could’ introduces an element of uncertainty, suggesting that victory is possible, but the outcome depends on the team’s strategic gameplay.
Can We Use Could for Present Tense?
While ‘could’ is typically associated with past and conditional situations, it can also be employed in the present tense when expressing weaker possibilities or potential events.
Examples
- She could solve complex math problems with some additional practice.
In this instance, ‘could’ suggests a present capability that is not fully realized, emphasizing the potential with additional effort.
Can We Use Could in Conditionals?
Indeed, ‘could’ finds its place in conditional statements, indicating hypothetical or less certain situations.
Examples
- If she studied harder, she could have aced the exam.
In this example, ‘could have’ is employed in a past hypothetical conditional, suggesting that acing the exam was possible if the condition (studying harder) had been fulfilled.
Could vs Can in a Question
Choosing between ‘could’ and ‘can’ in a question involves considering the level of formality and context. ‘Can’ is suitable for casual inquiries, while ‘could’ is more fitting for formal or polite questioning.
Examples
- Can: Can I borrow your notes for the class?
- Could: Could you please provide me with the agenda for the meeting?
In conclusion, mastering the nuances between ‘can’ and ‘could’ is vital to fluency in English. By understanding their distinct applications and reviewing examples, learners can navigate the subtleties of these modal verbs, enhancing their language proficiency and communication skills.
