Conjunctions like “because,” “even if,” “unless,” and “whereas” connect clauses and clarify relationships between ideas. Each serves a unique purpose in expressing reasons, conditions, or contrasts.
Understanding conjunctions enhances your writing by improving clarity and coherence. These words link thoughts, helping readers grasp complex ideas easily. “Because” provides reasons, while “even if” presents hypothetical situations. “Unless” introduces conditions, and “whereas” contrasts different elements. Mastering these conjunctions allows you to express yourself more effectively in both spoken and written communication.
By using them correctly, you can create engaging content that resonates with your audience and improves readability. This guide will delve into each conjunction, offering examples to illustrate their usage in everyday language.
Introduction To Conjunctions
Conjunctions are important words in sentences. They connect ideas and thoughts. The words because, even if, unless, and whereas serve different purposes.
Because explains the reasons. For example, “I stayed home because it was raining.”
Even if shows a condition. An example is, “I will go even if it snows.”
Unless sets a condition too. For instance, “I won’t eat unless I’m hungry.”
Whereas compares two ideas. For example, “I like tea, whereas she prefers coffee.”
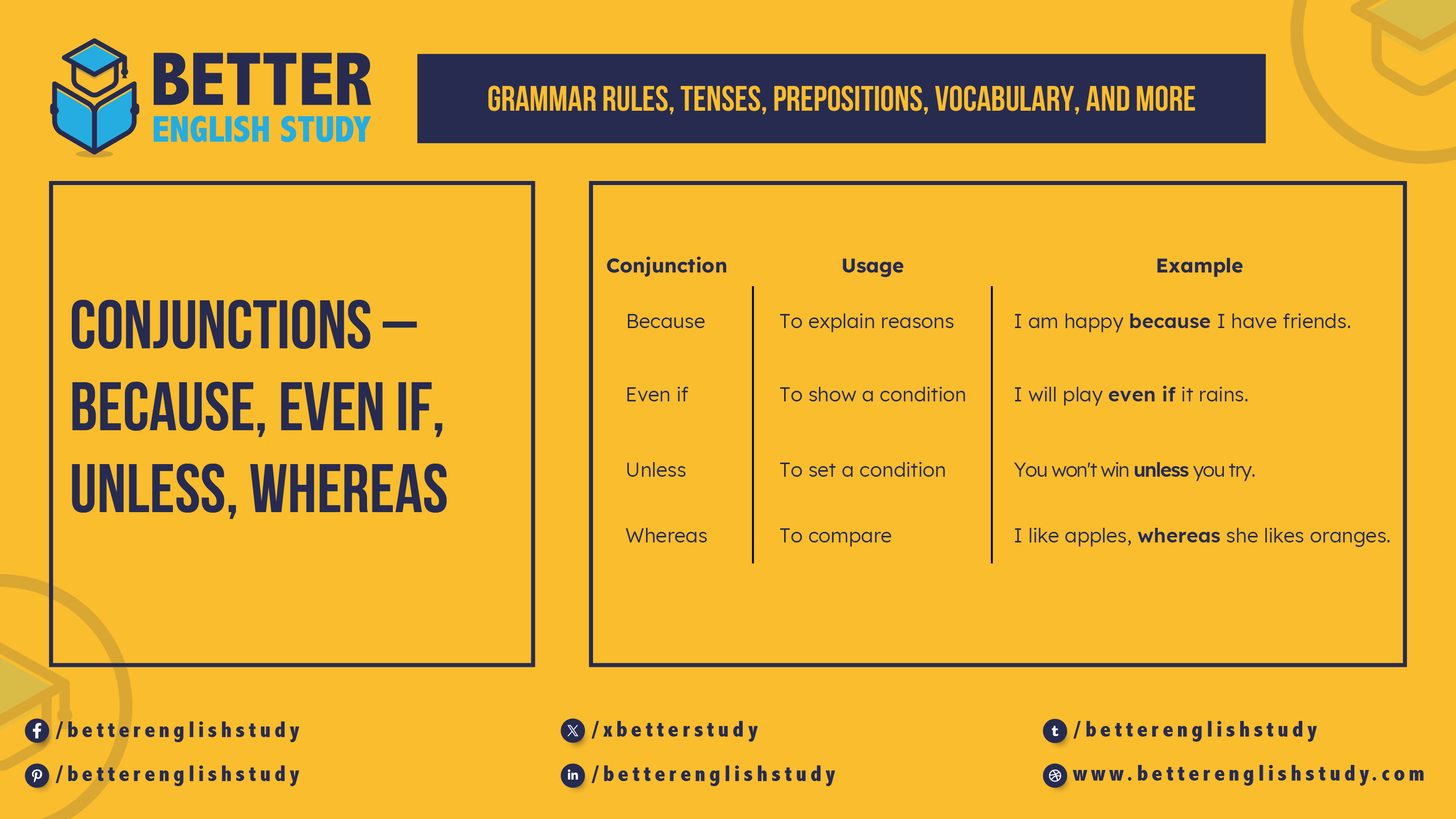
| Conjunction | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Because | To explain reasons | I am happy because I have friends. |
| Even if | To show a condition | I will play even if it rains. |
| Unless | To set a condition | You won’t win unless you try. |
| Whereas | To compare | I like apples, whereas she likes oranges. |
Diving Into ‘because’
Because is a conjunction used to show reasons. It connects two ideas. The first idea explains why the second idea happens.
For example, “I stayed home because it was raining.” Here, staying home is explained by the rain.
Another example is, “She was happy because she got a gift.” The gift made her happy. This word helps us understand why something occurs.
Using because helps clarify relationships between actions and feelings. It makes sentences stronger and more meaningful.
20 Example sentences using Because
- I stayed home because it was raining.
- She is happy because she passed the test.
- He is late because the bus broke down.
- They went to the park because it was sunny.
- I brought my umbrella because I thought it might rain.
- We left early because we had a long drive ahead.
- The dog is barking because it heard a noise.
- I am tired because I didn’t sleep well last night.
- She didn’t go swimming because the water was too cold.
- He wore a jacket because it was chilly outside.
- I couldn’t finish my homework because I ran out of time.
- They are having a party because it’s her birthday.
- I was late because my alarm didn’t go off.
- She is excited because she’s going on vacation.
- We stayed indoors because it was too hot outside.
- I bought the book because I love reading mysteries.
- He missed the train because he overslept.
- She is sad because her friend moved away.
- They went shopping because they needed new clothes.
- I didn’t eat lunch because I wasn’t hungry.

‘even If’ Unpacked
‘Even If’ is used to show a condition that does not change the outcome. It highlights situations where something remains true regardless of the circumstances.
For example, consider the sentence: “I will go for a walk even if it rains.” This means the rain won’t stop the walk.
Another example is: “She will help you even if she is busy.” This indicates her willingness to assist despite her schedule.
When crafting sentences with ‘Even If’, think about situations where one event does not affect another. Use it to express determination or commitment.
20 Example sentences using Even If
- I’ll go for a walk even if it’s raining.
- She will finish her work even if she’s tired.
- I’m going to the party even if I don’t know many people.
- He will run the race even if it’s very hot.
- They will visit us even if they are busy.
- She’ll wear her new dress even if it’s too cold.
- I’ll help you even if I’m not feeling well.
- He will try his best even if he doesn’t win.
- I’ll keep studying even if the test is hard.
- They will play soccer even if it starts to rain.
- She’ll stay positive even if things go wrong.
- He’ll travel tomorrow even if his flight is delayed.
- I’ll call you even if it’s late at night.
- They will keep dancing even if the music stops.
- I’ll visit the museum even if I’ve been there before.
- He will tell the truth even if it gets him in trouble.
- I’ll try the new food even if I don’t like how it looks.
- She will go to the meeting even if she has other plans.
- We’ll have fun even if it rains on our trip.
- He’ll keep working even if he’s feeling sick.
Exploring ‘unless’
Using ‘unless’ creates a condition that must be met. It means “except if.”
For example, “I will go outside unless it rains.” This shows that rain stops the action.
In communication, ‘unless’ helps clarify situations. It points out the conditions needed for something to happen.
For instance, “You won’t pass unless you study.” This indicates studying is crucial for passing.
Always remember, that ‘unless’ is a powerful word. It can change the meaning of a sentence. Therefore, using it correctly is important for clear communication.
20 Example sentences using Unless
- I won’t go to the party unless you come with me.
- She won’t pass the test unless she studies hard.
- We can’t start the meeting unless everyone is here.
- He won’t get better unless he takes his medicine.
- I won’t call you unless there’s an emergency.
- You can’t enter the room unless you have a key.
- They won’t play soccer unless the rain stops.
- The train won’t leave unless all passengers are on board.
- I can’t help you unless you tell me what’s wrong.
- She won’t eat her vegetables unless they’re cooked.
- He won’t be happy unless he wins the game.
- You won’t understand unless you listen carefully.
- I won’t go outside unless it stops snowing.
- They won’t believe you unless you show them proof.
- We won’t leave unless everyone is ready.
- He can’t finish the project unless he gets more time.
- I won’t forgive you unless you apologize.
- The door won’t open unless you push it hard.
- She won’t wear the dress unless it’s a special occasion.
- I won’t cook dinner unless you help me.
The Contrast Of ‘Whereas’
The word whereas shows a strong contrast between two ideas. It links sentences to highlight differences.
For example, “She loves ice cream, whereas he prefers cake.” This clearly shows their different choices.
Using whereas makes complex sentences easier to understand. It helps to compare and contrast in a simple way.
For instance, “The cat is playful, whereas the dog is calm.” This sentence clearly points out their unique traits.
When writing, try to use whereas to enhance clarity. It makes your writing more engaging. Always remember, it connects ideas effectively.
20 Example sentences using Whereas
- I prefer action movies, whereas my sister enjoys romantic comedies.
- He is tall, whereas his brother is quite short.
- My friend is a vegetarian, whereas I love eating meat.
- She likes warm weather, whereas her husband enjoys the cold.
- This city is noisy, whereas the countryside is peaceful.
- My brother plays basketball, whereas I prefer soccer.
- They like to stay up late, whereas I go to bed early.
- He enjoys classical music, whereas I prefer pop.
- The hotel is expensive, whereas the guesthouse is affordable.
- Some students study hard, whereas others barely prepare.
- He works in an office, whereas his wife works from home.
- The new model is lightweight, whereas the old one is heavy.
- She loves to dance, whereas her friends prefer singing.
- He is very outgoing, whereas she is more reserved.
- The store is open, whereas the café next door is closed.
- I like to eat at home, whereas they prefer dining out.
- She enjoys reading fiction, whereas he prefers non-fiction.
- The weather here is hot, whereas it’s much cooler in the mountains.
- He is very talkative, whereas his friend is quite shy.
- I like bright colors, whereas she prefers neutral tones.
Comparative Analysis
Conjunctions play an important role in connecting thoughts.
Because shows reasons. It answers the question “Why?” For example, “I stayed home because it rained.”
Even if introduces a condition that won’t change the outcome. For instance, “I will go even if it snows.” It expresses determination.
Unless means “if not.” It shows a condition needed for something to happen. For example, “I won’t eat unless I’m hungry.” It sets a clear limit.
Whereas compares two different situations. It highlights contrasts. An example is, “I like apples, whereas she prefers oranges.” This helps in understanding differences.
These conjunctions are useful in writing. They help clarify ideas and connections. Choosing the right conjunction can improve clarity in your sentences.
Practical Applications
Using conjunctions like “because,” “even if,” “unless,” and “whereas” improves clarity.
In academic writing:
Because explains the reasons clearly. For example, “I studied hard because I wanted to pass.”
Even if allows discussing possibilities. An example is, “I will go even if it rains.”
Unless shows conditions. For instance, “I won’t eat unless I am hungry.”
Whereas compares two ideas. For example, “I like pizza, whereas my brother likes sushi.”
In everyday conversation, these conjunctions make speech smoother.
Saying, “I love hiking, because it’s fun,” feels natural.
Use “even if” to express determination. For example, “I’ll go shopping even if it’s late.”
The word “unless” helps set limits. You might say, “I won’t play outside unless the weather is nice.”
“Whereas” can show differences in preferences. For instance, “I prefer dogs, whereas my friend likes cats.”
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Conjunctions Like “because” And “unless”?
Conjunctions like “because” and “unless” connect clauses or sentences. “Because” explains reasons, while “unless” indicates conditions. These words help clarify relationships between ideas, enhancing the flow of writing. Understanding their usage can improve both speaking and writing skills.
How Do I Use “even If” In A Sentence?
“Even if” introduces a condition that doesn’t change the main idea. For example, “I’ll go for a walk even if it rains. ” This shows determination despite possible obstacles. It emphasizes that the action will occur regardless of the situation.
Use it to express resilience in your writing.
Can “whereas” Show Contrast In Sentences?
Yes, “whereas” is used to contrast two ideas or statements. For example, “She loves classical music, whereas he prefers jazz. ” This conjunction highlights differences effectively. It can enhance clarity in comparisons and is useful in academic and formal writing.
Why Are Conjunctions Important In Writing?
Conjunctions are crucial for linking ideas smoothly. They provide clarity and coherence in writing. Using them correctly can enhance readability and help convey complex thoughts. This makes your writing more engaging and easier to understand for readers.
Conclusion
Understanding conjunctions like “because,” “even if,” “unless,” and “whereas” enhances your writing clarity. These words help connect ideas seamlessly. Using them effectively can elevate your communication skills. Practice incorporating these conjunctions in your writing. This will make your sentences more fluid and engaging, ultimately improving your overall message delivery.
