Imagine you’re telling a story about your best friend, Sarah. How often would you repeat her name in a conversation? Likely, you’d replace “Sarah” with “she” after the first mention. This simple swap between a noun and a pronoun is a fundamental aspect of English grammar.
Understanding the differences between nouns and pronouns is crucial for mastering the language.
Let’s delve into these two essential components of speech and explore their unique roles and characteristics.
Noun vs Pronoun: What is the Main Difference?
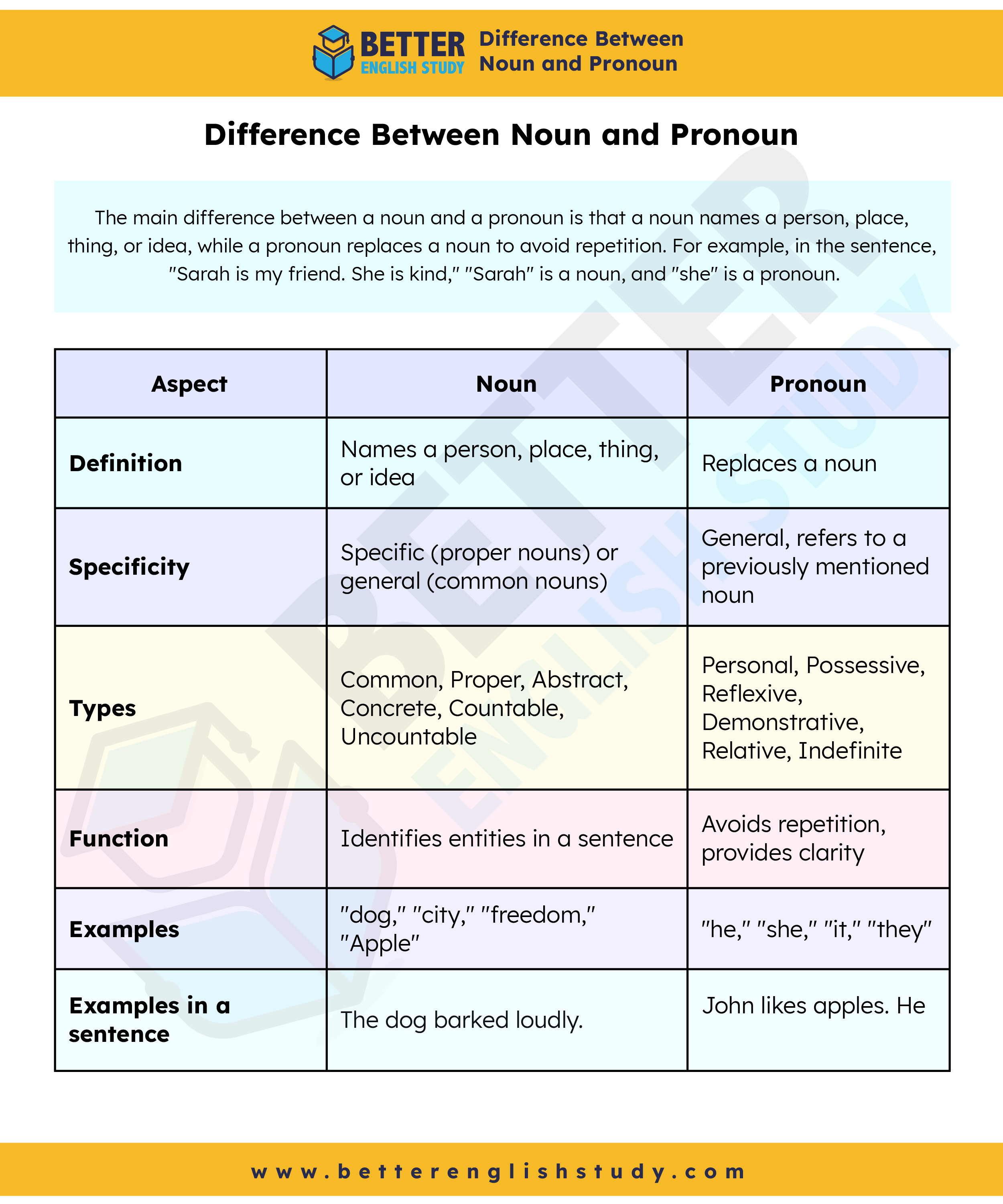
The main difference between a noun and a pronoun is that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea, while a pronoun replaces a noun to avoid repetition.
For example, in the sentence, “Sarah is my friend. She is kind,” “Sarah” is a noun, and “she” is a pronoun.
What is a Noun?
A noun is a word used to identify people, places, things, or ideas. Nouns are one of the building blocks of sentences, providing clarity and specificity to what we are talking about.
Types of Nouns
- Common Nouns
Common nouns refer to general items rather than specific ones. Examples include “city,” “dog,” and “book.” For instance, “The dog barked loudly.“
- Proper Nouns
Proper nouns name specific people, places, or things and are always capitalized. Examples are “New York,” “Einstein,” and “Google.” For example, “Einstein developed the theory of relativity.“
- Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns denote ideas, qualities, or states that cannot be seen or touched. Examples include “freedom,” “happiness,” and “time.” For example, “Freedom is a fundamental right.“
- Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns refer to things that can be perceived through the five senses. Examples are “apple,” “music,” and “car.” For instance, “The apple is on the table.“
- Countable Nouns
Countable nouns can be counted and have both singular and plural forms. Examples include “cat” (cats) and “house” (houses). For example, “I have three cats.“
- Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns cannot be counted and typically do not have a plural form. Examples are “water,” “rice,” and “advice.” For instance, “Water is essential for life.“
What is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun to avoid repetition and make sentences easier to understand. Pronouns must agree with the nouns they replace in number and gender.
Types of Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific persons or things. Examples include “he,” “she,” “it,” and “they.” For example, “Tom loves his dog. He takes it for a walk every day.“
- Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns show ownership or possession. Examples are “mine,” “yours,” “his,” and “hers.” For instance, “The book is mine.“
- Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence. Examples include “myself,” “yourself,” and “themselves.” For example, “She made herself a cup of tea.“
- Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific things. Examples are “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those.” For instance, “This is my favorite song.“
- Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. Examples include “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “which,” and “that.” For example, “The person who called you is my friend.“
- Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific persons or things. Examples are “someone,” “anything,” “each,” and “few.” For example, “Someone left their umbrella.“
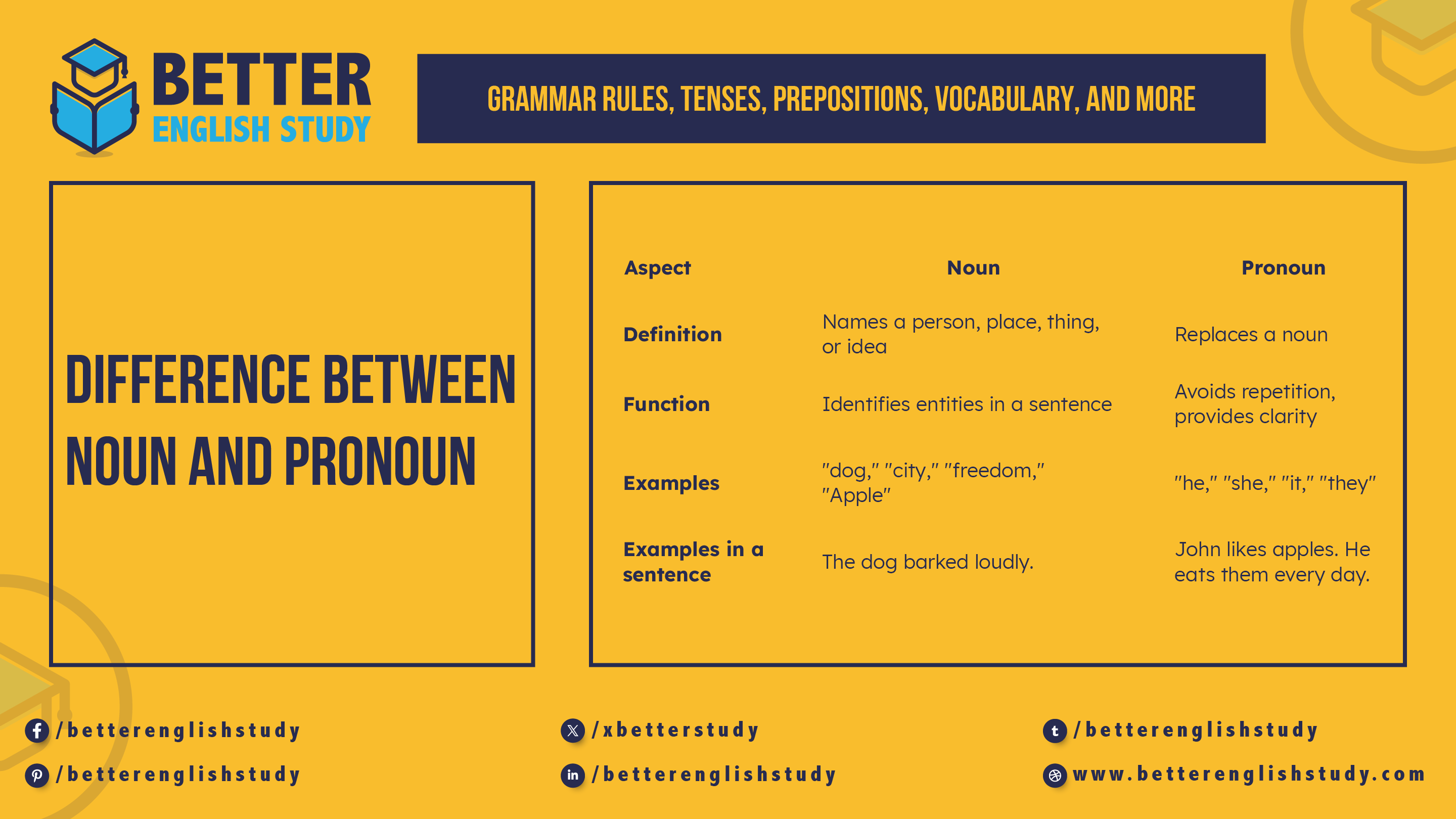
Difference Between Noun and Pronoun
Nouns and pronouns serve different purposes in a sentence. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Aspect | Noun | Pronoun |
| Definition | Names a person, place, thing, or idea | Replaces a noun |
| Specificity | Specific (proper nouns) or general (common nouns) | General, refers to a previously mentioned noun |
| Types | Common, Proper, Abstract, Concrete, Countable, Uncountable | Personal, Possessive, Reflexive, Demonstrative, Relative, Indefinite |
| Function | Identifies entities in a sentence | Avoids repetition, provides clarity |
| Examples | “dog,” “city,” “freedom,” “Apple” | “he,” “she,” “it,” “they” |
| Examples in a sentence | The dog barked loudly. | John likes apples. He eats them every day. |
Usage in Sentences
Nouns and Pronouns Together
In many sentences, nouns and pronouns are used together to provide clarity and avoid redundancy. Initially, a noun is introduced to identify the subject or object. Subsequently, a pronoun is used to refer back to that noun without repeating it, making the sentence smoother and more concise.
Example: John lost his wallet. He is looking for it.
Explanation:
- In the first sentence, “John” is the noun identifying the subject, and “wallet” is the noun identifying the object.
- In the second sentence, “He” is a pronoun replacing “John,” and “it” is a pronoun replacing “wallet.” This use of pronouns prevents the repetition of the nouns “John” and “wallet,” making the conversation more natural and fluid.
Pronouns Replacing Nouns
Pronouns are particularly useful in sentences to replace nouns that have already been mentioned, ensuring that the language does not become repetitive. This replacement helps to maintain the flow of communication and keeps the sentences from becoming cumbersome.
Example: Maria likes pizza. She eats it often.
Explanation:
- In the first sentence, “Maria” is the noun identifying the subject, and “pizza” is the noun identifying the object of her liking.
- In the second sentence, “She” is a pronoun replacing “Maria,” and “it” is a pronoun replacing “pizza.” This substitution streamlines the sentence, eliminating unnecessary repetition and keeping the focus on the action being described.
By understanding how nouns and pronouns can be used together or how pronouns can replace nouns, learners can construct sentences that are clear, concise, and easy to understand. This practice not only improves writing skills but also enhances verbal communication, making interactions more effective and engaging.
Can Nouns and Pronouns be Used in a Single Sentence?
Yes, nouns and pronouns are often used together in a sentence to provide clarity and avoid repetition.
For example, Lisa picked up her book and started reading it. Here, “Lisa” is a noun, and “her” and “it” are pronouns replacing “Lisa’s” and “book” respectively.
Understanding the differences between nouns and pronouns, along with their correct usage, is fundamental for effective communication in English. By practicing these basics, learners can enhance their language skills and express themselves more clearly and naturally.
