The past continuous tense describes actions that were ongoing in the past, while the past perfect continuous tense indicates actions that were ongoing before another past action. For example, “I was reading a book” (past continuous) contrasts with “I had been reading a book before dinner” (past perfect continuous).
Understanding the nuances of English tenses can enhance your writing clarity. The past continuous tense emphasizes the duration of an action happening at a specific moment. In contrast, the past perfect continuous tense focuses on the duration of an action leading up to another past event.
Mastering these tenses will help you convey your thoughts more accurately. Clear communication is essential in both spoken and written English, making tense usage crucial for effective expression.
Introduction To Past Tenses
Understanding the basics of past tenses is essential for mastering English grammar. There are different types of past tenses, including Past Continuous and Past Perfect Continuous. Each serves a unique purpose in storytelling and communication.
Past Continuous Tense describes actions happening at a specific time in the past. For example, “I was reading a book.” This shows an ongoing action.
On the other hand, Past Perfect Continuous Tense focuses on actions that were ongoing before another action. An example is, “I had been studying for three hours.” This indicates the duration of an action before something else occurs.
Both tenses are important for clarity in sentences. Using them correctly enhances your ability to express ideas accurately.
Diving Into Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense describes actions that were happening at a specific time in the past. It is formed using the past tense of the verb “to be” plus the -ing form of the main verb. For example, “I was reading” or “They were playing.” This tense shows that an action was ongoing and might have been interrupted.
Use the Past Continuous Tense for key situations. It describes actions in progress, background actions, or simultaneous activities. For instance, “While I was studying, my brother was watching TV.” This tense can also show interrupted actions: “She was cooking when the phone rang.” It helps to create a vivid picture of the past.
Exploring Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense shows an action that continued until another action happened. This tense emphasizes the duration of an action. It is formed using had been + present participle (verb + ing).
For example, “She had been studying for three hours before the exam started.” This shows the action of studying was ongoing.
Key situations for using this tense include:
- To show an action that was ongoing before a specific time in the past.
- To indicate the cause of a past situation.
- When describing repeated actions that occurred until another action happened.
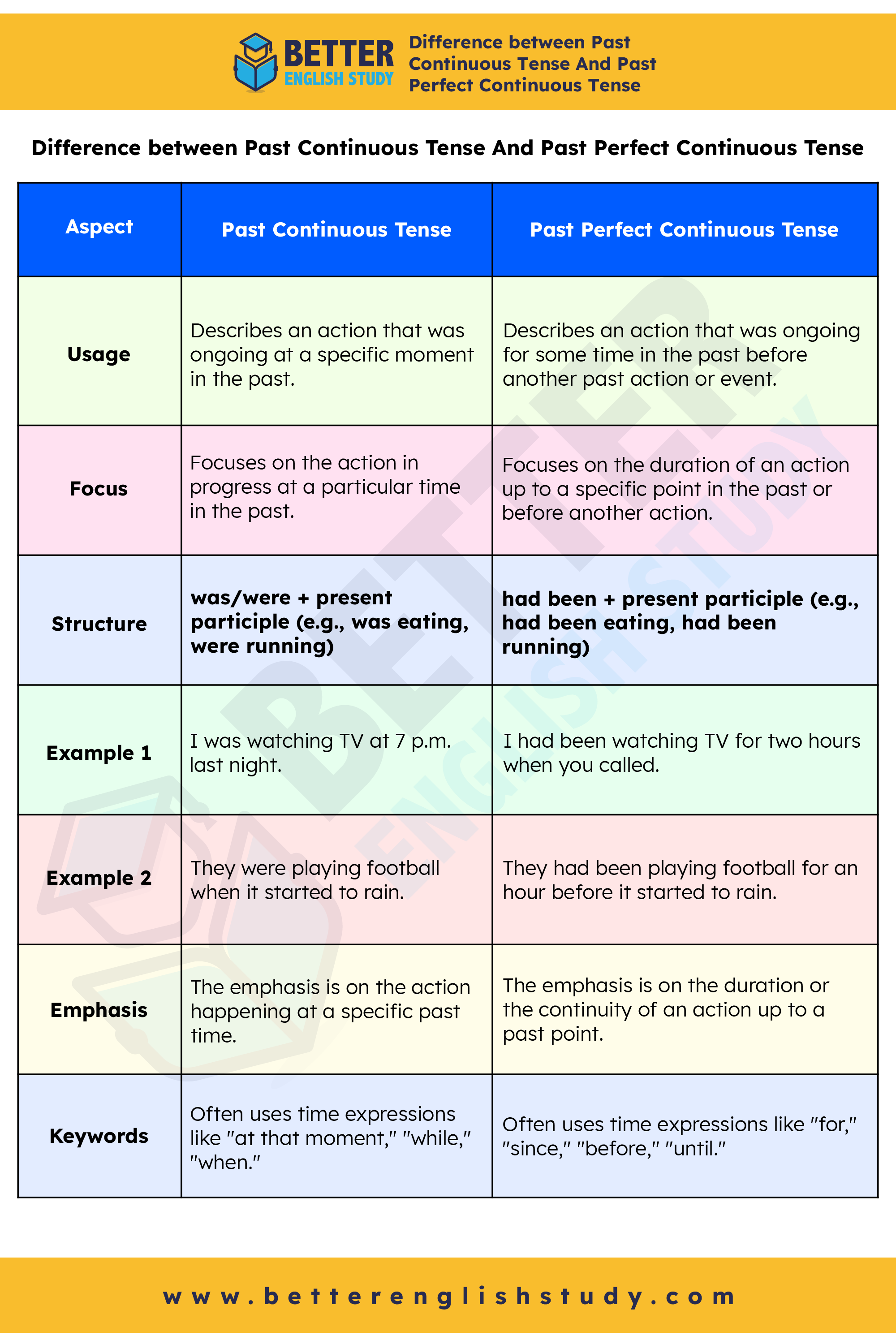
Difference between Past Continuous Tense And Past Perfect Continuous Tense
| Aspect | Past Continuous Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes an action that was ongoing at a specific moment in the past. | Describes an action that was ongoing for some time in the past before another past action or event. |
| Focus | Focuses on the action in progress at a particular time in the past. | Focuses on the duration of an action up to a specific point in the past or before another action. |
| Structure | was/were + present participle (e.g., was eating, were running) | had been + present participle (e.g., had been eating, had been running) |
| Example 1 | I was watching TV at 7 p.m. last night. | I had been watching TV for two hours when you called. |
| Example 2 | They were playing football when it started to rain. | They had been playing football for an hour before it started to rain. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on the action happening at a specific past time. | The emphasis is on the duration or the continuity of an action up to a past point. |
| Keywords | Often uses time expressions like “at that moment,” “while,” “when.” | Often uses time expressions like “for,” “since,” “before,” “until.” |
- Past continuous describes actions that were happening at a specific point in the past.
- Past perfect continuous focuses on actions that were happening over a period of time before another past action.
Examples In Practice
The Past Continuous Tense shows actions that were happening at a specific time in the past. For example, “I was reading a book.” This indicates that the reading was ongoing.
Another example is, “They were playing soccer.” Here, the action of playing was in progress.
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense highlights actions that were ongoing before another action in the past. For instance, “I had been studying for two hours.” This shows that studying happened before something else.
Another example is, “She had been working there for five years.” The working was continuous until a certain point.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Mixing up the tenses can lead to confusion. The past continuous tense shows an action that was ongoing. For example, “I was reading.” The past perfect continuous tense indicates an action that happened before another action. An example is, “I had been reading.” It’s important to use the correct tense for clarity.
Overcomplicating the usage of these tenses can create mistakes. Use past continuous for actions in progress. Use past perfect continuous for actions completed before another action. Keep sentences simple to avoid confusion. This makes writing clearer and easier to understand.
Tips For Mastering These Tenses
Practicing exercises helps in mastering the past continuous and past perfect continuous tenses. Try these examples:
- Write sentences using “was/were + verb + ing.”
- Use “had been + verb + ing” for past perfect continuous.
- Identify the main action in each tense.
Real-life applications make learning fun. Use these tenses in daily conversations:
- Talk about what you were doing at a specific time.
- Share stories about actions that started and continued in the past.
Practice with friends. Create dialogues using both tenses. This enhances understanding and retention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Past Continuous Tense?
The past continuous tense describes actions that were ongoing in the past. It is formed using “was/were” followed by the verb ending in “-ing. ” For example, “I was reading. ” This tense emphasizes the duration of an action rather than its completion.
How Is Past Perfect Continuous Tense Formed?
The past perfect continuous tense is formed using “had been” followed by the verb ending in “-ing. ” For instance, “She had been studying. ” This tense highlights an action that started in the past and continued up to another point in the past.
When To Use Past Continuous Tense?
Use the past continuous tense to indicate interrupted actions. It sets the scene or describes background activities. For example, “I was watching TV when the phone rang. ” This shows that the action was ongoing until another event occurred.
When To Use Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
Use the past perfect continuous tense to show an action that was ongoing before another action in the past. For instance, “They had been playing soccer for hours before it started to rain. ” This indicates a continuous action prior to a specific moment.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between past continuous and past perfect continuous tenses is essential for effective communication. Each tense serves a unique purpose in storytelling and describing events. By grasping these concepts, you can enhance your writing skills and convey your thoughts more clearly.
Practice using these tenses to master their applications.
