The Past Continuous Tense describes ongoing actions in the past, while the Past Perfect Tense indicates actions completed before another past event. For example, “I was studying” illustrates ongoing action, whereas “I had studied” shows completion before another event.
Understanding the nuances of different tenses is essential for effective communication. The Past Continuous Tense emphasizes the duration of an action, often setting the scene for events in storytelling. On the other hand, the Past Perfect Tense clarifies the sequence of actions, making it clear which event occurred first.
Mastering these tenses enhances writing clarity and improves narrative flow. By using these tenses correctly, you can convey time relationships more effectively in your writing.
Introduction To Past Tenses
Understanding tenses is crucial for mastering English. They help express time and actions clearly.
The past continuous tense describes actions that were happening at a certain time. For example, “I was reading a book.” This shows the action in progress.
The past perfect tense highlights actions completed before another action. For instance, “I had finished my homework.” This indicates that the homework was done before something else occurred.
| Tense | Example | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Past Continuous | I was playing soccer. | Action in progress in the past. |
| Past Perfect | I had eaten lunch. | Action completed before another past action. |
Diving Into Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense describes actions happening in the past. It shows ongoing events. This tense is formed using the verb “to be” and the -ing form of the main verb.
For example, “I was reading a book” indicates an action in progress. This tense often emphasizes the duration of an event.
| Forming the Past Continuous | Example |
|---|---|
| Subject + was/were + verb(-ing) | I was playing soccer. |
| Subject + was/were not + verb(-ing) | She was not watching TV. |
| Was/Were + subject + verb(-ing)? | Were they studying math? |
Use the Past Continuous to describe background actions. It can show interrupted actions too. For example, “I was walking when it started to rain.” This highlights a past event that interrupted another.
Exploring Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense shows actions that happened before another action in the past. It is formed using “had” plus the past participle of the verb. For example, “She had eaten” shows that eating happened before another event.
Use the Past Perfect Tense to clarify the order of events. It helps avoid confusion. For instance, “He had left before I arrived” clearly states that leaving happened first.
Common scenarios for using this tense include:
- Describing actions completed before a specific time.
- Indicating a cause for a past situation.
- Showing that one action interrupted another.
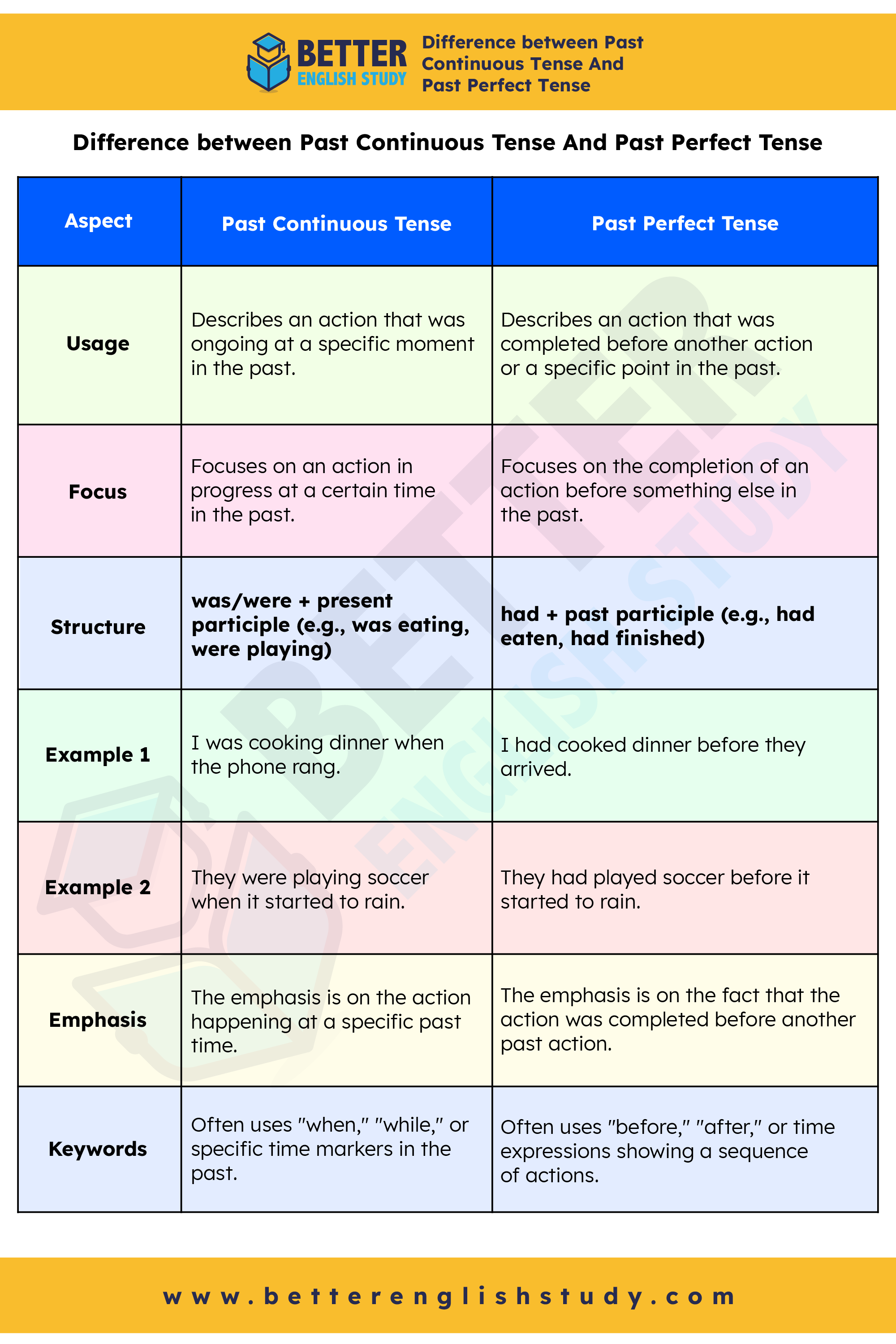
Difference between Past Continuous Tense And Past Perfect Tense
| Aspect | Past Continuous Tense | Past Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes an action that was ongoing at a specific moment in the past. | Describes an action that was completed before another action or a specific point in the past. |
| Focus | Focuses on an action in progress at a certain time in the past. | Focuses on the completion of an action before something else in the past. |
| Structure | was/were + present participle (e.g., was eating, were playing) | had + past participle (e.g., had eaten, had finished) |
| Example 1 | I was cooking dinner when the phone rang. | I had cooked dinner before they arrived. |
| Example 2 | They were playing soccer when it started to rain. | They had played soccer before it started to rain. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on the action happening at a specific past time. | The emphasis is on the fact that the action was completed before another past action. |
| Keywords | Often uses “when,” “while,” or specific time markers in the past. | Often uses “before,” “after,” or time expressions showing a sequence of actions. |
- Past continuous describes actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past.
- Past perfect describes actions that were completed before a certain time or event in the past.
Examples To Clarify
Understanding the difference between past continuous and past perfect tenses is essential for clear communication. Past continuous describes ongoing actions in the past, while past perfect indicates actions completed before another past event. Examples help illustrate these distinctions effectively.
Past Continuous In Action
The past continuous tense describes actions that were happening at a specific time. For example, “I was reading a book.” This shows the action of reading was ongoing. Another example is, “They were playing football.” This indicates the action of playing was in progress.
Past Perfect In Context
The past perfect tense shows actions that happened before another action in the past. For instance, “I had finished my homework.” This means homework was completed before something else happened. Another example is, “She had left the party.” This indicates she left before another event occurred.
Common Mistakes And How To Avoid Them
Many writers confuse the past continuous tense and past perfect tense. Mixing up these tenses can lead to unclear sentences. The past continuous shows an action that was ongoing in the past. For example, “I was reading a book.” It highlights the action’s duration.
The past perfect tense describes an action completed before another action in the past. For instance, “I had finished my homework before dinner.” This shows the order of events clearly.
Overusing the past perfect can confuse readers. Use it only when necessary. Remember, clarity is key to effective writing. Keep sentences simple and straightforward for better understanding.
Tips For Mastering Past Tenses
To master past tenses, practice is key. Use practice exercises to improve your skills. Focus on the differences between past continuous and past perfect tenses. Here are some helpful tips:
- Write sentences using both tenses.
- Identify the time indicators in each sentence.
- Use examples from stories or personal experiences.
Real-life application helps to understand these tenses better. Try to notice when people speak in past tenses. Listen for the context and how each tense is used.
| Tense | Example |
|---|---|
| Past Continuous | I was reading a book. |
| Past Perfect | I had finished my homework. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Past Continuous Tense?
Past Continuous Tense describes actions that were ongoing in the past. It emphasizes the duration or interruption of an action. For example, “I was reading when she called. ” This tense often sets the scene for another event that occurred.
How Is Past Perfect Tense Used?
Past Perfect Tense indicates that an action was completed before another action in the past. It highlights the sequence of events. For instance, “She had finished her homework before dinner. ” This tense helps clarify the timeline of multiple past actions.
What Are Examples Of Past Continuous Tense?
Examples of Past Continuous Tense include sentences like “I was walking,” or “They were playing soccer. ” These sentences show actions in progress at a specific time in the past. This tense helps create a vivid picture of past events.
What Are Examples Of Past Perfect Tense?
Examples of Past Perfect Tense include “He had left before I arrived” and “They had studied for weeks. ” These sentences demonstrate actions that occurred before a specific moment in the past. This tense provides clarity in describing the order of events.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between past continuous and past perfect tenses enhances your writing clarity. Each tense serves a unique purpose in storytelling. By using these tenses correctly, you can convey time relationships effectively. Practice with the examples provided, and soon, mastering these tenses will become second nature.
Happy writing!
