
The Past Perfect Tense indicates an action completed before another past action, while the Past Perfect Continuous Tense emphasizes the duration of an action up to a certain point in the past. For example, “She had finished her homework” (Past Perfect) versus “She had been studying for hours” (Past Perfect Continuous).
Understanding verb tenses is crucial for effective communication. The Past Perfect Tense and the Past Perfect Continuous Tense serve distinct purposes in storytelling and writing. The Past Perfect Tense helps clarify the sequence of events, showing which action occurred first.
In contrast, the Past Perfect Continuous Tense highlights ongoing actions that were happening before a specific moment in the past. Mastering these tenses can elevate your writing, making it more precise and engaging.
Introduction To Past Perfect Tenses
The Past Perfect Tense shows an action completed before another past action. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner.” This tense uses “had” plus the past participle of the verb.
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense emphasizes the duration of an action that was ongoing before another past event. For instance, “They had been playing soccer for two hours when it started to rain.” This tense uses “had been” plus the present participle of the verb.
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Past Perfect | Had + Past Participle | She had eaten breakfast. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Had been + Present Participle | He had been studying all night. |
Key Features Of Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense is used to show that an action was completed before another action. It often uses the auxiliary verb “had” followed by the past participle of the main verb. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner.” This structure clearly shows the order of events.
Common usage scenarios include describing actions in stories. For instance, “He had left before she arrived.” This highlights that one action happened before the other.
Understanding its formulation helps in mastering English. It allows for clearer communication about time and sequence. Practicing different examples can enhance your grasp of this tense.
Exploring Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense shows actions that continued up to a specific time in the past. It emphasizes the duration of an action. This tense is formed using “had been” plus the verb in the -ing form.
Example: “She had been studying for hours before the test.” This shows she started studying earlier.
Typical use cases for this tense include:
- To show an action that was ongoing before another past action.
- To indicate the duration of an action in the past.
- To express a situation that had a cause and effect relationship.
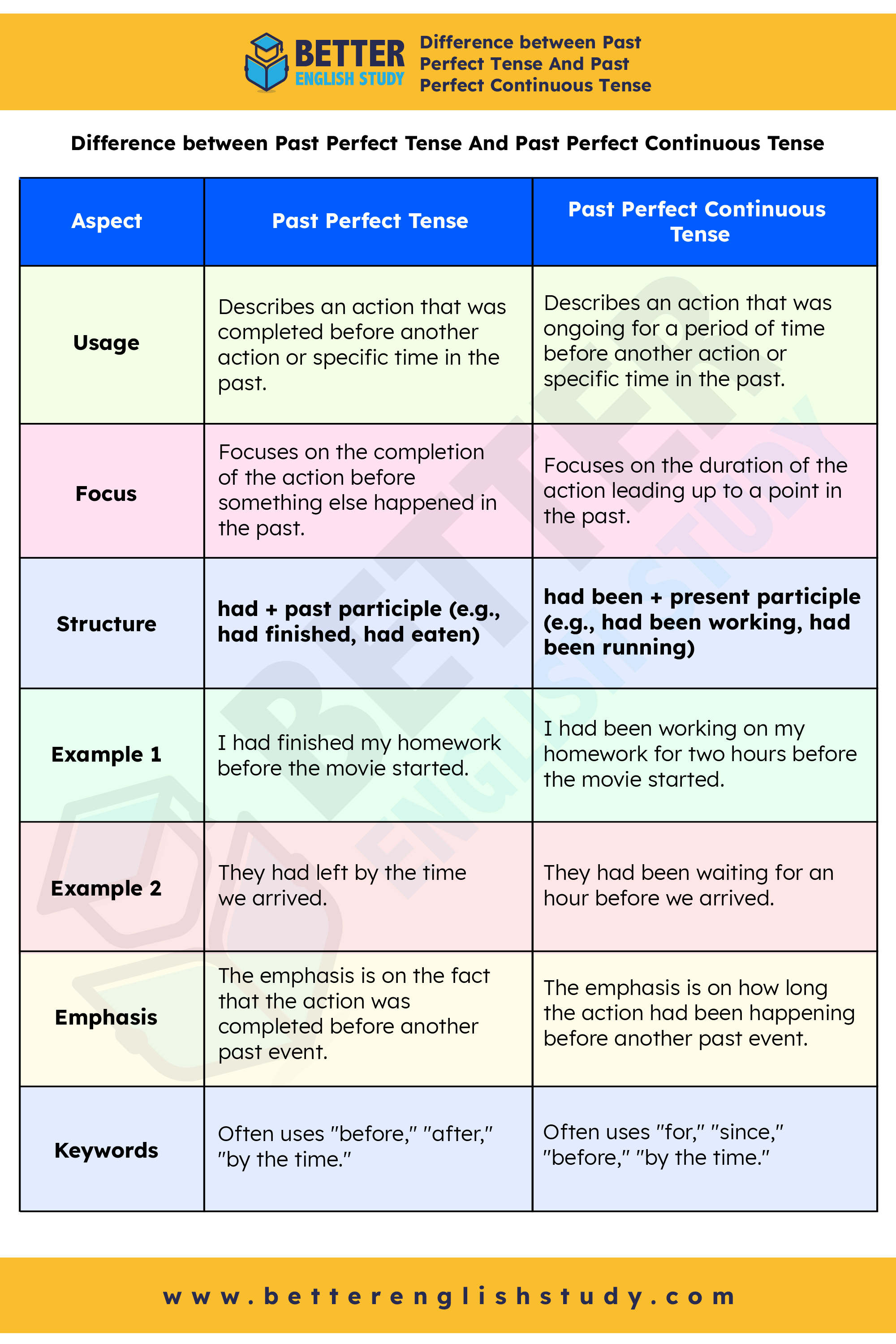
Difference between Past Perfect Tense And Past Perfect Continuous Tense
| Aspect | Past Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes an action that was completed before another action or specific time in the past. | Describes an action that was ongoing for a period of time before another action or specific time in the past. |
| Focus | Focuses on the completion of the action before something else happened in the past. | Focuses on the duration of the action leading up to a point in the past. |
| Structure | had + past participle (e.g., had finished, had eaten) | had been + present participle (e.g., had been working, had been running) |
| Example 1 | I had finished my homework before the movie started. | I had been working on my homework for two hours before the movie started. |
| Example 2 | They had left by the time we arrived. | They had been waiting for an hour before we arrived. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on the fact that the action was completed before another past event. | The emphasis is on how long the action had been happening before another past event. |
| Keywords | Often uses “before,” “after,” “by the time.” | Often uses “for,” “since,” “before,” “by the time.” |
- Past perfect describes actions that were completed before another past action or time.
- Past perfect continuous highlights the duration of an action up until another past event.
Practical Examples
Understanding the difference between the past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense is crucial for clear communication. Practical examples illustrate how actions relate in time, enhancing your grammar skills. Explore these distinctions to improve your writing and speaking proficiency.
Past Perfect In Action
The past perfect tense shows actions that happened before another action. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner.” Here, “had finished” is the past perfect. It emphasizes that her homework was complete first.
Another example is, “They had left the party before it started to rain.” This sentence highlights that their departure happened before the rain.
Past Perfect Continuous In Context
The past perfect continuous tense shows actions that were ongoing before another action. For instance, “He had been studying for hours before the test.” This indicates his study time was continuous up to the test.
Another example is, “They had been waiting for the bus when it arrived.” This shows their waiting was ongoing at that moment.
Common Mistakes And Misconceptions
Many learners confuse past perfect tense with past perfect continuous tense. This leads to common mistakes in writing and speaking. Remember, the past perfect tense describes an action completed before another past action. For example, “She had finished her homework.” It shows completion.
On the other hand, the past perfect continuous tense emphasizes the duration of an action before another past event. An example is “She had been studying for three hours.” This indicates an ongoing action up to a point in the past.
One frequent error is using the wrong tense in sentences. Avoid saying, “She had been finished her work.” Instead, say “She had finished her work.” Using the correct form helps convey the right meaning.
Another misconception involves mixing the two tenses. Saying “I had been played soccer” is incorrect. The correct phrase is “I had played soccer.” Keep these differences in mind for better clarity.
Conclusion And Summary
Understanding the difference between Past Perfect Tense and Past Perfect Continuous Tense is essential.
Past Perfect Tense shows an action that was completed before another action. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner.” This tense focuses on the completion of the action.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense emphasizes an action that was ongoing before another action. For instance, “They had been playing soccer before it started to rain.” This tense highlights the duration of the action.
Key points include:
- Past Perfect Tense: completed actions.
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense: ongoing actions.
- Use both tenses to express time relationships clearly.
Understanding these differences helps in using tenses correctly in writing and speaking.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Past Perfect Tense?
The past perfect tense describes an action completed before another past action. It uses “had” plus the past participle of the verb. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner. ” This tense emphasizes the sequence of events in the past.
How Does Past Perfect Continuous Differ?
The past perfect continuous tense focuses on the duration of an action before another past event. It uses “had been” plus the present participle. For example, “He had been studying for hours before the exam started. ” This highlights the ongoing nature of the action prior to the interruption.
When Should I Use Past Perfect Tense?
Use the past perfect tense when you need to clarify the order of events. It’s particularly useful in storytelling. For instance, “They had left before the storm hit. ” This structure helps prevent confusion about which event occurred first.
Can You Give Examples Of Both Tenses?
Certainly! For past perfect, consider “She had already left when I arrived. ” For past perfect continuous, “They had been working for months before the project ended. ” These examples illustrate how each tense serves a different purpose in conveying time.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense is essential for clear communication. Each tense serves a unique purpose in expressing time and continuity. By mastering these tenses, you can enhance your writing and speaking skills.
Practice using them in sentences to reinforce your understanding.
