The past perfect tense indicates an action completed before another past action, while the present perfect tense describes an action that occurred at an unspecified time before now. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner” uses past perfect, whereas “She has finished her homework” employs present perfect.
Understanding verb tenses is crucial for clear communication. The past perfect tense focuses on actions completed in the past relative to another event. It often clarifies the sequence of events, helping to avoid confusion. On the other hand, the present perfect tense connects past actions to the present, emphasizing their relevance now.
Mastering these tenses enhances your writing and speaking skills, making your messages more precise and effective.
Introduction To Perfect Tenses
The perfect tense shows actions related to time. It helps us understand when something happened. Two main types are past perfect and present perfect. Each serves a unique purpose in communication.
The past perfect tense indicates an action completed before another action in the past. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner.” This shows the order of events clearly.
The present perfect tense connects past actions to the present. An example is, “I have eaten breakfast.” This implies the action affects the current moment. Understanding these tenses is crucial for effective communication.
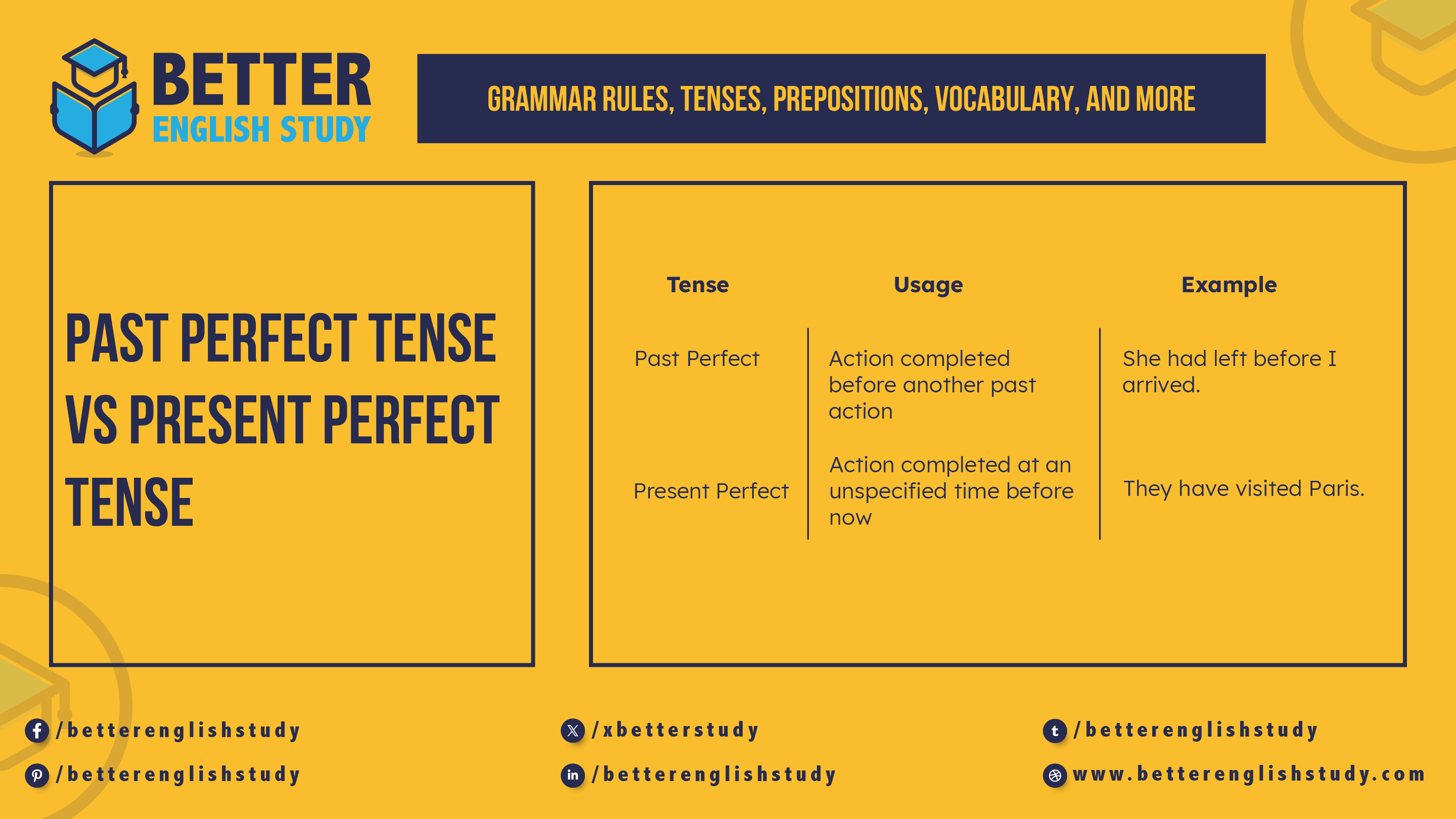
| Tense | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Past Perfect | Action completed before another past action | She had left before I arrived. |
| Present Perfect | Action completed at an unspecified time before now | They have visited Paris. |
Basics Of Past Perfect Tense
To form the past perfect tense, use “had” plus the past participle of the verb. For example, “had eaten” or “had played.” This tense shows an action completed before another past action.
Key uses include:
- Describing an action finished before another past action.
- Explaining reasons for a past event.
- Creating a timeline of events.
Examples:
- She had finished her homework before dinner.
- They had left before the rain started.
- He had never seen the movie until last night.
Exploring Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense shows actions that happened at an unspecified time. It connects the past to the present. This tense uses the verb “have” or “has” with the past participle of the main verb.
To form the present perfect tense, follow this structure:
| Subject | Have/Has | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| I/You/We/They | have | finished |
| He/She/It | has | eaten |
Key uses include actions that started in the past but continue now. For example, “I have lived here for five years.” Another example is “She has seen that movie.” These show how the present relates to the past.
Difference between Past Perfect Tense And Present Perfect Tense
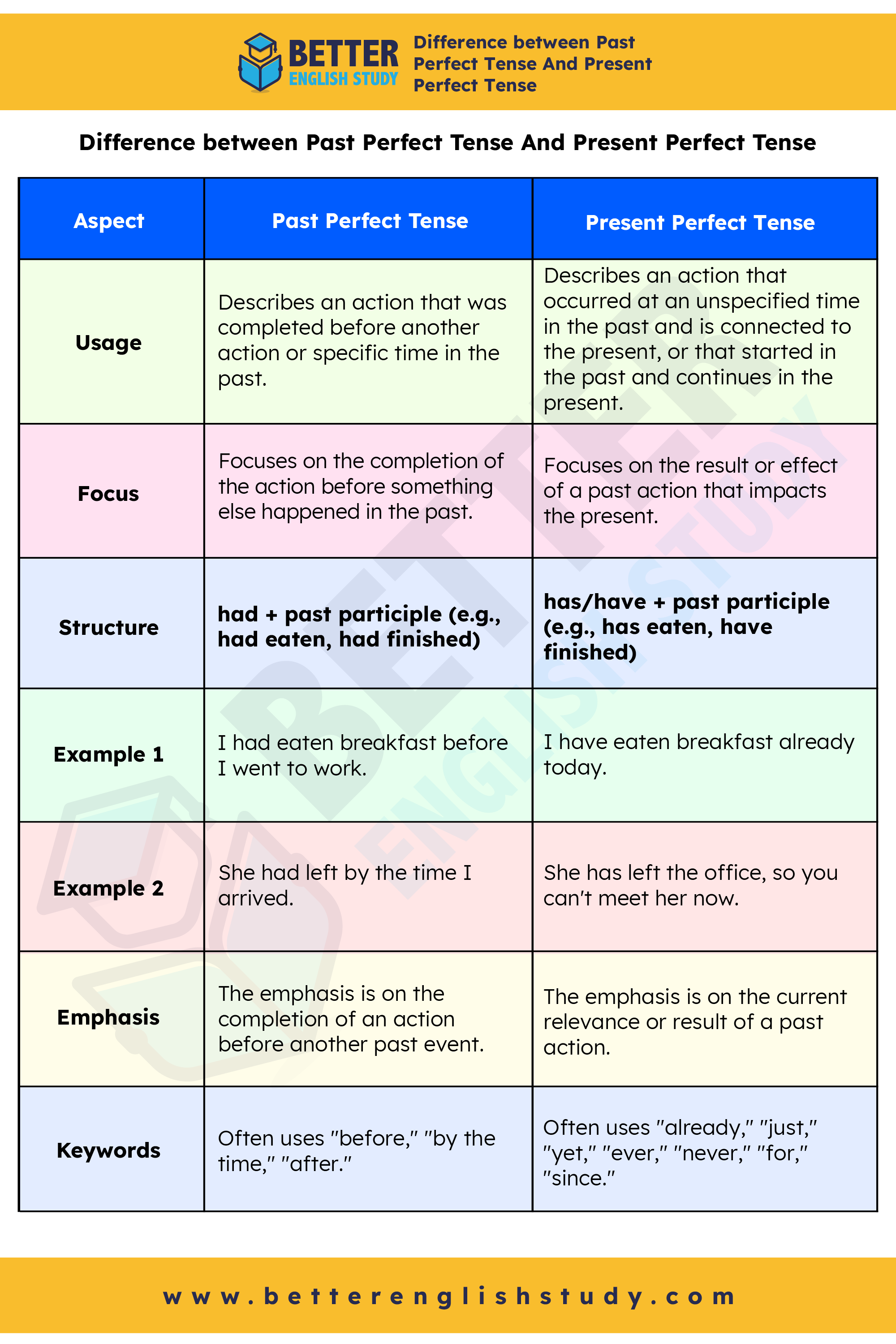
| Aspect | Past Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes an action that was completed before another action or specific time in the past. | Describes an action that occurred at an unspecified time in the past and is connected to the present, or that started in the past and continues in the present. |
| Focus | Focuses on the completion of the action before something else happened in the past. | Focuses on the result or effect of a past action that impacts the present. |
| Structure | had + past participle (e.g., had eaten, had finished) | has/have + past participle (e.g., has eaten, have finished) |
| Example 1 | I had eaten breakfast before I went to work. | I have eaten breakfast already today. |
| Example 2 | She had left by the time I arrived. | She has left the office, so you can’t meet her now. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on the completion of an action before another past event. | The emphasis is on the current relevance or result of a past action. |
| Keywords | Often uses “before,” “by the time,” “after.” | Often uses “already,” “just,” “yet,” “ever,” “never,” “for,” “since.” |
- Past perfect describes actions that were completed before another action in the past.
- Present perfect describes actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past but have relevance to the present or actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
Common Confusions And Clarifications
Many people confuse past perfect tense and present perfect tense. The past perfect tense shows an action completed before another past action. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner.” In contrast, the present perfect tense connects past actions to the present. An example is, “They have lived here for five years.”
Common misconceptions include thinking both tenses are interchangeable. They serve different purposes and should be used correctly. To avoid mistakes, practice using examples. Recognize the timeline of each action. Focus on the time frame when using these tenses.
Here are some tips:
- Identify if the action is complete or ongoing.
- Use time markers like “before” or “since.”
- Practice with simple sentences.
Practical Applications In Everyday English
Using the past perfect tense in storytelling helps show actions completed before another past action. For example, “She had left before he arrived.” This clearly indicates her departure happened first.
The present perfect tense expresses experiences without specifying when they occurred. For instance, “I have visited Paris.” This indicates an experience that is relevant now.
In storytelling, the past perfect tense adds depth. It helps readers understand the sequence of events clearly. The present perfect tense connects past experiences to the present moment.
These tenses are essential in everyday English. They allow speakers to express time and experiences effectively.
Exercises And Practice
Interactive exercises help in understanding the difference between Past Perfect and Present Perfect tenses. These activities can include fill-in-the-blank sentences and matching exercises.
Real-life application scenarios show how to use these tenses. For example, when telling a story, use the Past Perfect to describe actions completed before another action. Use Present Perfect to talk about experiences up to now.
| Scenario | Example |
|---|---|
| Past Perfect | She had finished her homework before dinner. |
| Present Perfect | I have visited Paris three times. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Past Perfect Tense?
The Past Perfect Tense describes an action completed before another past action. It emphasizes the sequence of events. For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner. ” This tense helps clarify timelines in storytelling and enhances the reader’s understanding of events.
How Is Present Perfect Tense Used?
The Present Perfect Tense indicates actions that occurred at an unspecified time before now. It connects past actions to the present. For instance, “I have visited Paris. ” This tense is useful for discussing experiences, changes, or actions that continue into the present.
What Are Examples Of Past Perfect Tense?
Examples of the Past Perfect Tense include sentences like “They had left before the rain started. ” Another example is “He had already eaten when she arrived. ” These examples show actions completed before another event in the past, providing clarity in communication.
What Are Examples Of Present Perfect Tense?
Examples of the Present Perfect Tense include “She has read that book. ” Another example is “We have lived here for five years. ” These sentences illustrate completed actions relevant to the present, highlighting experiences or ongoing situations.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between past perfect and present perfect tenses enhances your writing skills. Each tense serves a unique purpose in conveying time and sequence. By practicing with examples, you can master their usage. This knowledge will improve both your speaking and writing, making your communication clearer and more effective.
