
The Past Simple Tense describes completed actions at a specific time in the past. The Present Perfect Tense indicates actions that occurred at an unspecified time or have relevance to the present.
Understanding the difference between Past Simple and Present Perfect Tense is crucial for effective communication. The Past Simple Tense is used for actions that started and finished in the past, often accompanied by time expressions like “yesterday” or “last year.”
In contrast, the Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present, using phrases like “have done” or “has lived. ” Mastering these tenses enhances writing and speaking skills, making your language more precise. Whether narrating a story or discussing experiences, knowing when to use each tense adds clarity to your communication.
Introduction To Tenses
Understanding tenses is key to mastering English grammar. Tenses help show when actions happen. The Past Simple Tense tells about actions that are finished. For example, “I walked to school yesterday.” This tense focuses on a specific time.
The Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present. It shows that something happened at an unspecified time. For example, “I have walked to school.” This tense emphasizes the experience rather than the exact time.
Both tenses are important. They help us express time clearly. Knowing the difference helps in communication and writing.
Past Simple Tense
The Past Simple Tense is used to describe actions that are completed in the past. It often indicates a specific time when the action took place.
Key characteristics include the use of regular and irregular verbs. Regular verbs end in -ed, while irregular verbs change form. For example, “walk” becomes “walked.”
Common uses involve telling stories, describing events, or stating facts. It answers questions like “What happened?” or “When did it occur?”
Example sentences:
1. She visited her grandmother last week.
2. They played soccer yesterday.
3. He finished his homework two days ago.
Present Perfect Tense
Understanding the difference between Past Simple and Present Perfect Tense is essential for clear communication. The Past Simple describes completed actions, while the Present Perfect connects past events to the present. For example, “I visited Paris” contrasts with “I have visited Paris.” Each tense serves a unique purpose in storytelling.
Definition
The present perfect tense describes actions that happened at an unspecified time. It connects the past with the present. This tense uses “have” or “has” plus the past participle of the verb.
Key Characteristics
- Focuses on results or effects in the present.
- Uses time expressions like “ever,” “never,” and “just.”
- Indicates actions that started in the past but continue now.
Common Uses
- To talk about experiences.
- To show actions that happened recently.
- For actions that occurred at an unknown time.
Example Sentences
- I have visited France.
- She has just finished her homework.
- They have never seen a giraffe.
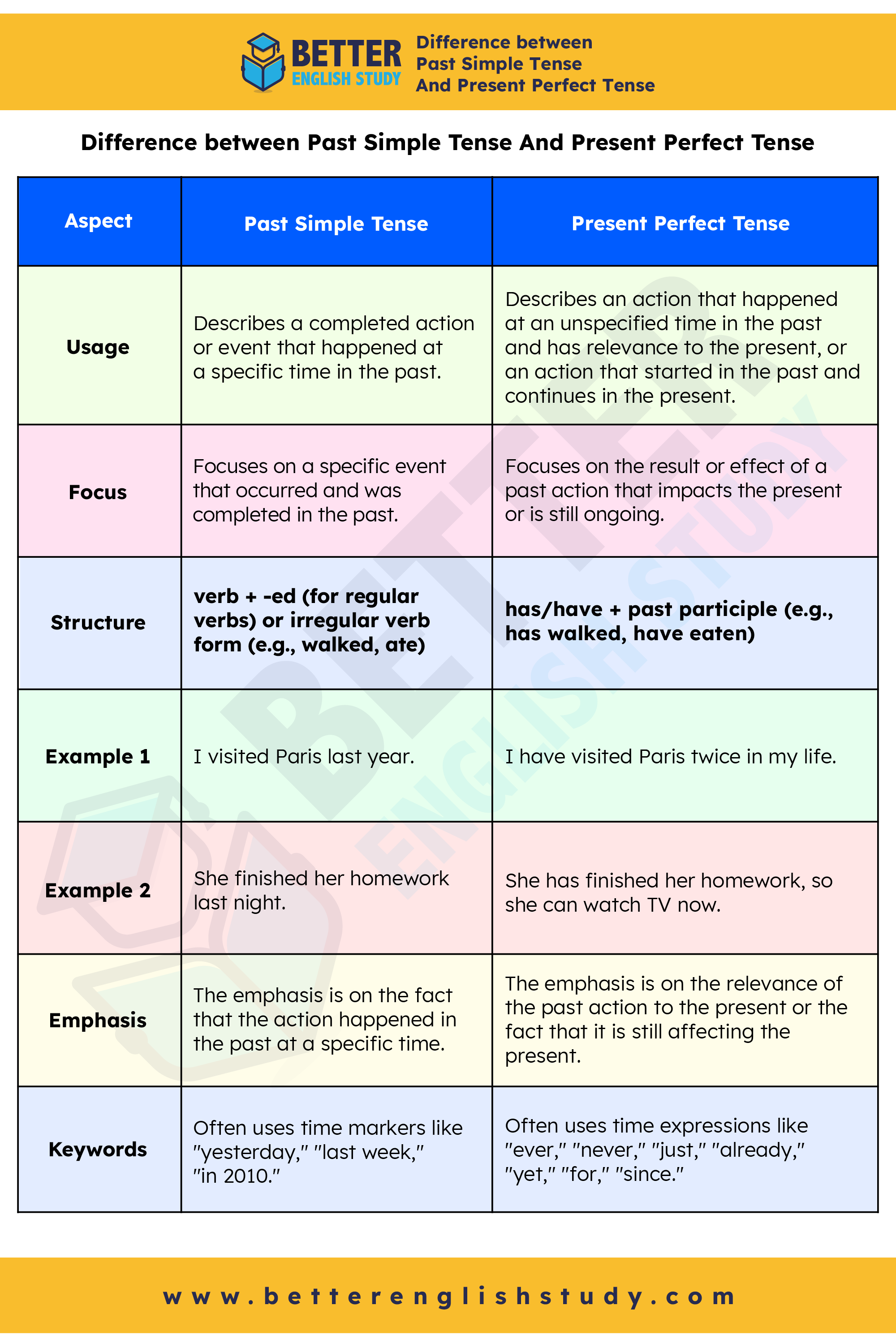
Difference between Past Simple Tense And Present Perfect Tense
| Aspect | Past Simple Tense | Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes a completed action or event that happened at a specific time in the past. | Describes an action that happened at an unspecified time in the past and has relevance to the present, or an action that started in the past and continues in the present. |
| Focus | Focuses on a specific event that occurred and was completed in the past. | Focuses on the result or effect of a past action that impacts the present or is still ongoing. |
| Structure | verb + -ed (for regular verbs) or irregular verb form (e.g., walked, ate) | has/have + past participle (e.g., has walked, have eaten) |
| Example 1 | I visited Paris last year. | I have visited Paris twice in my life. |
| Example 2 | She finished her homework last night. | She has finished her homework, so she can watch TV now. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on the fact that the action happened in the past at a specific time. | The emphasis is on the relevance of the past action to the present or the fact that it is still affecting the present. |
| Keywords | Often uses time markers like “yesterday,” “last week,” “in 2010.” | Often uses time expressions like “ever,” “never,” “just,” “already,” “yet,” “for,” “since.” |
- Past simple describes actions that happened and were completed at a specific time in the past.
- Present perfect describes actions that occurred at an unspecified time but are relevant to the present or actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
Forming Sentences
The Past Simple Tense is formed with the past form of the verb. For example, “I played soccer.” It shows actions that happened at a specific time in the past.
The Present Perfect Tense uses “has” or “have” plus the past participle of the verb. For instance, “I have played soccer.” It connects the past action to the present.
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Past Simple | Subject + past verb | I visited Paris. |
| Present Perfect | Subject + has/have + past participle | I have visited Paris. |
Pronunciation can vary between these tenses. In Past Simple, the ending sounds like “ed” in played. In Present Perfect, the focus is on the auxiliary verb, like in have or has.
Practical Applications
Using the Past Simple Tense in storytelling creates a sense of time. It describes events that happened in the past. For example, “She went to the park.” This tense helps to set the scene clearly.
The Present Perfect Tense is useful in academic writing. It connects the past with the present. An example is, “Researchers have found new evidence.” This shows ongoing relevance.
In everyday conversation, the Past Simple Tense helps share experiences. For instance, “I saw a movie yesterday.” It makes the story clear and direct.
The Present Perfect Tense is also common in daily chats. Phrases like, “I have visited France,” show life experiences. This makes conversations more engaging.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Many learners often misuse time expressions. The past simple tense refers to a specific time. For example, “I visited Paris last year.” The present perfect tense describes actions without a specific time. For instance, “I have visited Paris.” Mixing these can lead to confusion.
Confusing usage is common. The past simple tense tells what happened before. The present perfect tense connects past actions to the present. Saying, “I have finished my homework yesterday” is incorrect. It should be “I finished my homework yesterday.”
Non-native speakers should focus on key tips. Practice using time expressions correctly. Always remember to connect events properly. Reading and listening to native speakers helps a lot. Regular practice builds confidence and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Past Simple Tense?
The Past Simple Tense describes actions completed at a specific time in the past. For example, “I visited Paris last year. ” It often uses regular or irregular verb forms. This tense emphasizes when an action occurred, making it clear that it is not ongoing.
How Does Present Perfect Tense Differ?
The Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present. For instance, “I have visited Paris. ” This tense indicates experiences or actions without specifying when they occurred. It focuses on the relevance of past actions in the current context.
When To Use Past Simple Vs. Present Perfect?
Use Past Simple for completed actions at a specific time. Use Present Perfect for actions with relevance to the present or that occurred at an unspecified time. Understanding these differences helps clarify your communication in English.
Can You Give Examples Of Both Tenses?
Sure! For Past Simple, “She finished her homework yesterday” is a clear example. For Present Perfect, “They have traveled to Japan” indicates an experience relevant now. Examples highlight how each tense functions in different contexts.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between the Past Simple and Present Perfect tenses is crucial for effective communication. Each tense serves a unique purpose in expressing time and experience. By mastering their usage, you can enhance your writing and speaking skills. Practice with examples to reinforce your understanding and boost your confidence.
