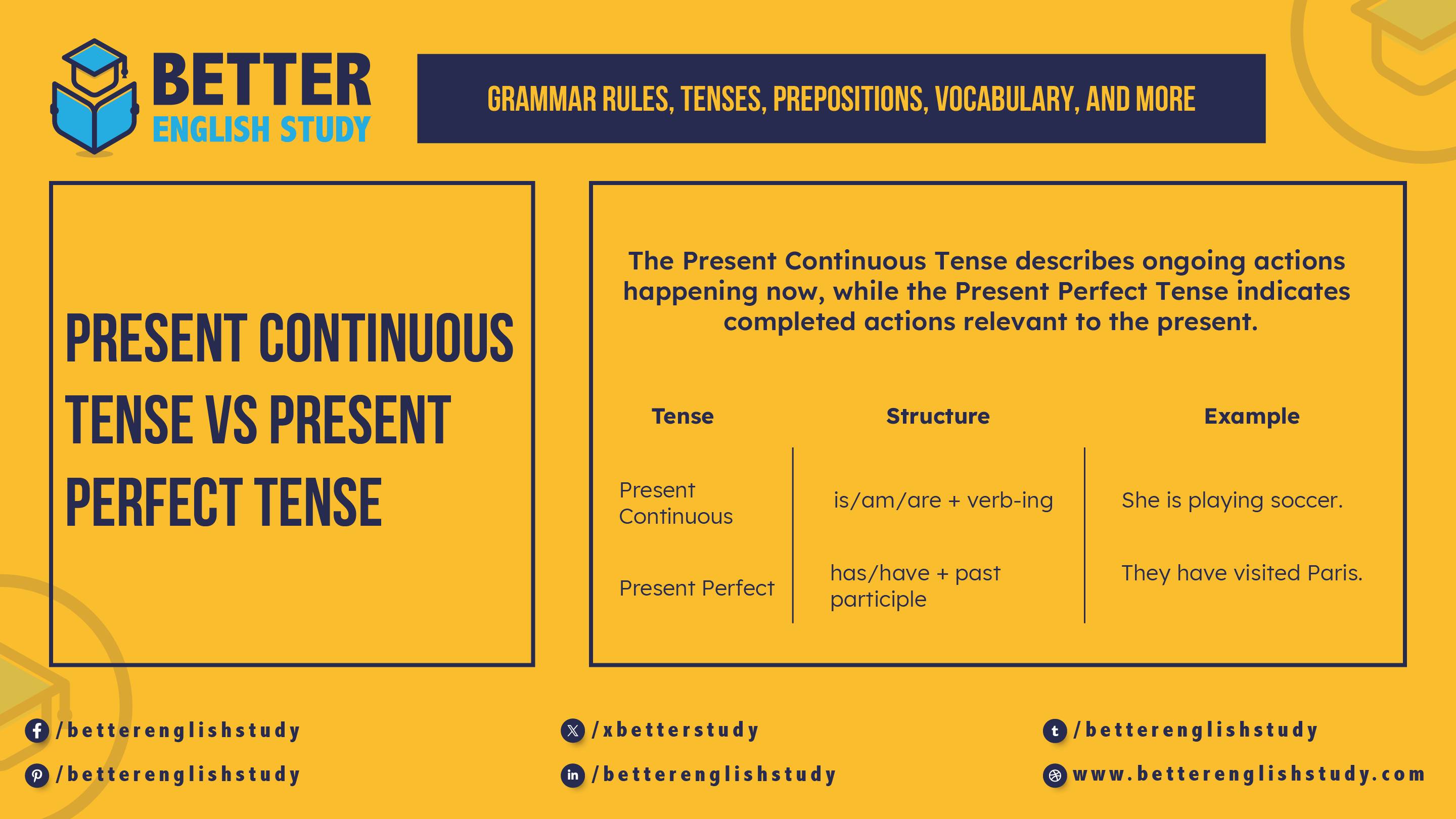
The Present Continuous Tense describes ongoing actions happening now, while the Present Perfect Tense indicates completed actions relevant to the present. For example, “I am studying” (Present Continuous) and “I have studied” (Present Perfect) highlight these differences.
Understanding verb tenses is essential for effective communication in English. The Present Continuous Tense focuses on actions currently in progress, making it useful for describing immediate situations. On the other hand, the Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present, emphasizing their relevance or impact.
Mastering these tenses helps convey time and context accurately, enhancing both spoken and written language skills. By distinguishing between these two tenses, learners can express thoughts clearly and engage their audience more effectively.
Introduction To Present Tenses
The Present Continuous Tense describes actions happening right now. It uses the verb “to be” and the main verb ending in “-ing.” For example, “She is reading a book.” This tense shows ongoing activities or future plans.
The Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present. It uses “has” or “have” with the past participle of the verb. An example is, “They have finished their homework.” This tense highlights completed actions with relevance to now.
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Continuous | is/am/are + verb-ing | She is playing soccer. |
| Present Perfect | has/have + past participle | They have visited Paris. |
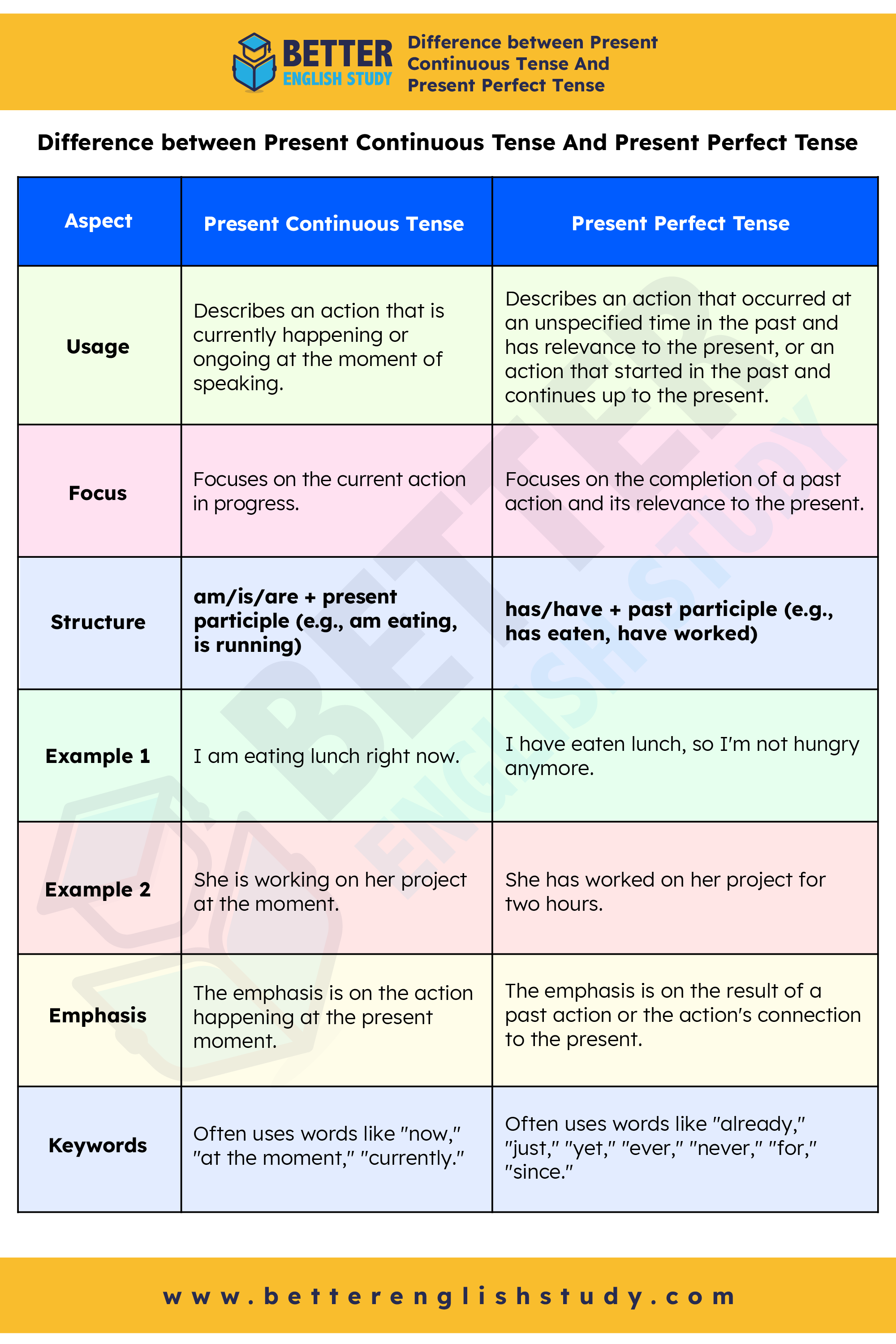
Difference between Present Continuous Tense And Present Perfect Tense
| Aspect | Present Continuous Tense | Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes an action that is currently happening or ongoing at the moment of speaking. | Describes an action that occurred at an unspecified time in the past and has relevance to the present, or an action that started in the past and continues up to the present. |
| Focus | Focuses on the current action in progress. | Focuses on the completion of a past action and its relevance to the present. |
| Structure | am/is/are + present participle (e.g., am eating, is running) | has/have + past participle (e.g., has eaten, have worked) |
| Example 1 | I am eating lunch right now. | I have eaten lunch, so I’m not hungry anymore. |
| Example 2 | She is working on her project at the moment. | She has worked on her project for two hours. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on the action happening at the present moment. | The emphasis is on the result of a past action or the action’s connection to the present. |
| Keywords | Often uses words like “now,” “at the moment,” “currently.” | Often uses words like “already,” “just,” “yet,” “ever,” “never,” “for,” “since.” |
- Present continuous describes actions happening right now or ongoing at the moment of speaking.
- Present perfect describes actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past but are relevant to the present or have continued up to the present.
Forming Present Continuous Tense
To form the Present Continuous Tense, use the verb “to be” and the main verb with an “-ing” ending. The structure looks like this:
| Subject | To Be | Main Verb (-ing) |
|---|---|---|
| I | am | eating |
| You | are | running |
| He/She/It | is | playing |
| We/They | are | studying |
Common verbs used in this tense include eating, running, and playing. These verbs show actions happening right now. This tense helps express ongoing actions clearly.
Forming Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using the auxiliary verb “have” or “has” plus the past participle of the main verb. The structure looks like this:
| Subject | Auxiliary Verb | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| I/You/We/They | have | played |
| He/She/It | has | played |
Here are some key verbs used in the Present Perfect Tense:
- have
- become
- know
- see
- work
Using these verbs helps create the Present Perfect Tense easily.
Usage Of Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense describes actions happening right now. For example, “She is running.” This shows an action in progress. It can also describe future plans. For instance, “They are meeting tomorrow.” This indicates a scheduled event.
When talking about ongoing actions, we often use this tense. It highlights what people are currently doing. You might say, “I am studying for my test.” This indicates an action that is still happening.
In terms of future arrangements, this tense is useful too. Saying, “We are going to the park next week” shows a planned activity. This helps clarify what will happen later.
Usage Of Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is used for completed actions. These actions have relevance to the present. For example, “I have eaten breakfast.” This shows that breakfast is done now. Another example is, “She has visited France.” This tells us she went there before now.
It is also used for life experiences. People use this tense to share what they have done. For instance, “I have seen a lion.” This means the experience happened at some point in life. Another example is, “He has learned to swim.” This shows he knows how to swim now.
Examples In Sentences
Understanding the difference between present continuous and present perfect tenses can enhance your English skills. Present continuous describes ongoing actions, like “I am studying. ” In contrast, present perfect indicates completed actions, as seen in “I have studied. ” Each tense serves a unique purpose in communication.
Present Continuous Examples
She is reading a book right now. They are playing soccer in the park. I am studying for my math test. We are watching a movie this evening.
Present Perfect Examples
I have finished my homework. They have traveled to many countries. She has eaten lunch already. We have seen that movie before.
Common Errors And Tips
Many people confuse time expressions with the present continuous and present perfect tenses. This often leads to miscommunication.
For example, saying “I am living here for five years” is incorrect. The correct form is “I have lived here for five years.” The present perfect shows actions that started in the past and continue now.
Common mistakes include using phrases like “just,” “yet,” and “since” in the wrong tense. For instance, “I am just finished my homework” should be “I have just finished my homework.”
Avoiding overgeneralization is also important. Each tense has its own rules. Make sure to practice and understand their specific uses.
Quiz And Practice
Identify the tense in the following sentences. Is it present continuous or present perfect?
- She is reading a book.
- They have completed their homework.
- He is playing soccer right now.
- We have visited the museum.
- It is raining outside.
Correct the errors in these sentences:
- I have seeing the movie.
- She is cooked dinner.
- They has finished their project.
- We are going to the park.
- He have played the guitar.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Present Continuous Tense?
The Present Continuous Tense describes actions happening right now or ongoing situations. It is formed using “am,” “is,” or “are” followed by the verb’s -ing form. For example, “I am writing. ” This tense emphasizes the current nature of an action, making it dynamic and immediate.
What Is The Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present. It is formed using “has” or “have” plus the past participle of the verb. For instance, “I have completed my homework. ” This tense highlights experiences or actions that affect the present moment, showcasing their relevance today.
How Do I Form Present Continuous Tense?
To form the Present Continuous Tense, use the appropriate form of “to be” (am, is, are) plus the verb ending in -ing. For example, “She is reading a book. ” This structure indicates ongoing actions and can express future plans as well, like “They are meeting us tomorrow.”
How Do I Form Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using “has” or “have” with the past participle of the verb. For example, “They have traveled to France. ” This structure indicates completed actions that have a link to the present, making it valuable for discussing life experiences.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between the present continuous tense and the present perfect tense is essential for effective communication. Each tense serves a unique purpose in conveying time and action. By practicing with examples, you can enhance your writing and speaking skills.
Mastering these tenses will improve your overall language proficiency.
