
The Present Perfect Tense expresses completed actions with relevance to the present, while the Present Perfect Continuous Tense emphasizes ongoing actions or experiences. For example, “I have read the book” indicates completion, while “I have been reading the book” highlights the ongoing process.
Understanding the difference between Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous tenses is vital for effective communication in English. These tenses help convey time and the nature of actions clearly. The Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present, making it essential for discussing experiences or achievements.
On the other hand, the Present Perfect Continuous Tense focuses on the duration or ongoing nature of actions. Mastering these tenses enhances your writing and speaking skills, allowing for more nuanced expression.
Introduction To Present Perfect And Present Perfect Continuous Tenses
The Present Perfect Tense describes actions that happened at an unspecified time. It connects the past to the present. For example, “I have eaten breakfast.” This shows breakfast was eaten but does not say when.
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense highlights actions that started in the past and continue to the present. It focuses on the duration of the action. An example is, “I have been eating breakfast for an hour.” This indicates the action has been ongoing.
Formulating Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense shows actions that happened at an unspecified time. It often connects the past with the present. The formula is: Subject + has/have + past participle.
Examples include:
- I have eaten breakfast.
- She has visited London.
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense emphasizes the duration of an action. It uses: Subject + has/have been + verb-ing.
Examples include:
- I have been studying for two hours.
- They have been playing soccer.
Both tenses serve different purposes. Understanding their usage helps improve writing.
Formulating Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense shows actions that started in the past and continue now. It often emphasizes the duration of an activity. To form this tense, use the structure: subject + has/have been + verb-ing.
For example, “She has been reading for two hours.” This indicates she started reading earlier and is still reading. Another example is, “They have been playing soccer all afternoon.” This shows the action is ongoing.
Key verbs often used include work, study, and run. Use this tense to highlight ongoing actions and their impact on the present.
Common Uses Of Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense shows actions that are completed at some point in time. It connects the past with the present. For example, “I have eaten lunch.” This means lunch is finished now.
Another use is to express experience. This tense tells what someone has done. For example, “She has traveled to Japan.” This shows her experience without saying when it happened.
Using this tense helps in conversations. It allows people to share their past actions easily. Understanding it helps everyone communicate better.
Common Uses Of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense describes actions that started in the past and continue now. It shows the duration of an activity. For example, “I have been studying for three hours.” This sentence highlights how long the studying has been happening.
This tense often uses keywords like “for” and “since.” They help indicate the length of time. For instance, “She has been playing soccer since morning.” It shows she started playing earlier and is still active.
Using this tense makes it clear that the action is still ongoing. It focuses on the activity’s impact on the present moment. For example, “They have been working hard all week.” This sentence implies they are still working hard now.
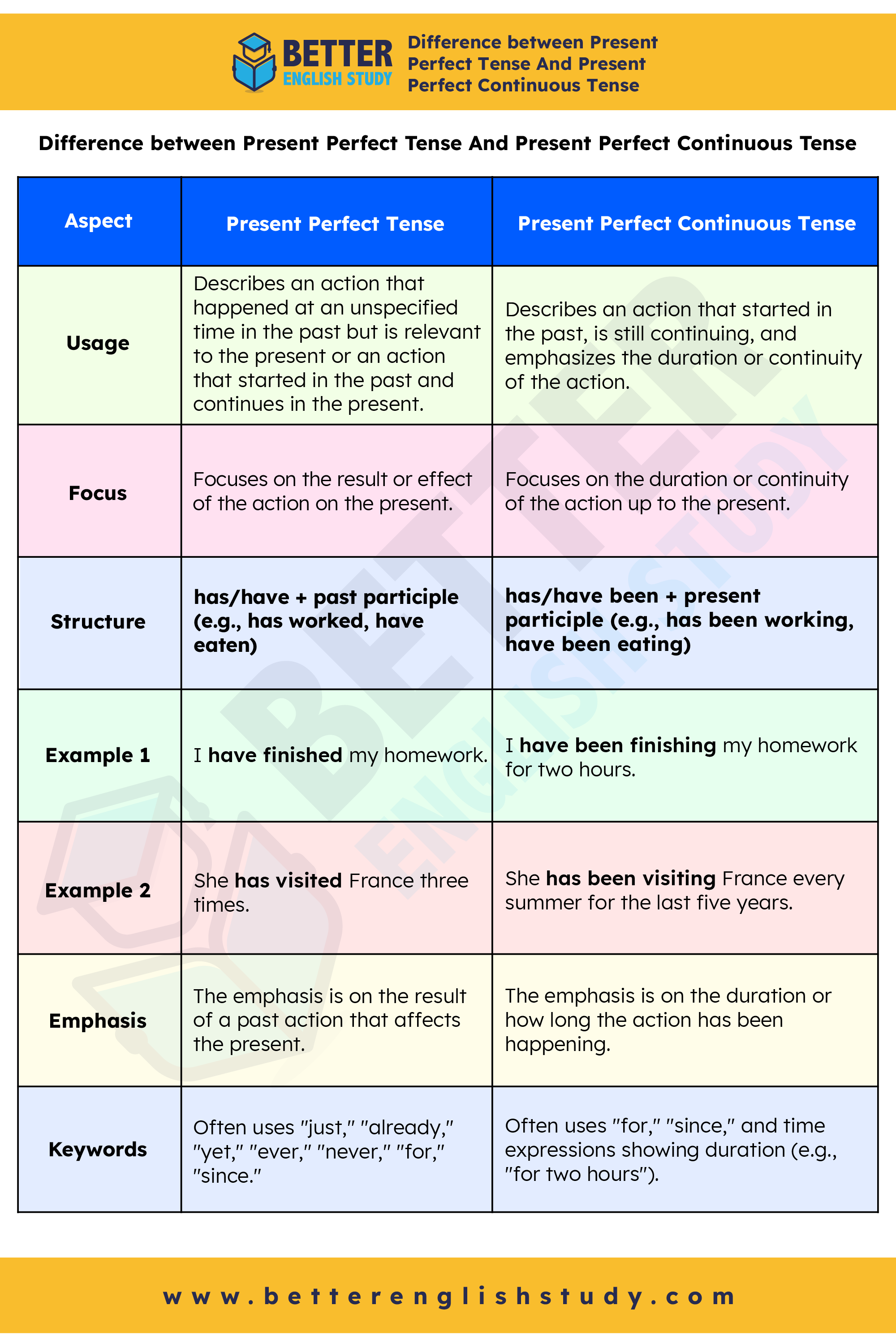
Difference between Present Perfect Tense And Present Perfect Continuous
| Aspect | Present Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes an action that happened at an unspecified time in the past but is relevant to the present or an action that started in the past and continues in the present. | Describes an action that started in the past, is still continuing, and emphasizes the duration or continuity of the action. |
| Focus | Focuses on the result or effect of the action on the present. | Focuses on the duration or continuity of the action up to the present. |
| Structure | has/have + past participle (e.g., has worked, have eaten) | has/have been + present participle (e.g., has been working, have been eating) |
| Example 1 | I have finished my homework. | I have been finishing my homework for two hours. |
| Example 2 | She has visited France three times. | She has been visiting France every summer for the last five years. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on the result of a past action that affects the present. | The emphasis is on the duration or how long the action has been happening. |
| Keywords | Often uses “just,” “already,” “yet,” “ever,” “never,” “for,” “since.” | Often uses “for,” “since,” and time expressions showing duration (e.g., “for two hours”). |
- Present perfect describes actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past but have relevance to the present or actions that started in the past and continue into the present, focusing on the result.
- Present perfect continuous emphasizes the duration or continuity of an action that started in the past and is still happening in the present.
Choosing Between Present Perfect And Present Perfect Continuous
Choosing the correct tense is important in English. The Present Perfect Tense is used for actions that are complete. It connects the past with the present. For example, “I have finished my homework.” This shows the action is done now.
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense focuses on actions that are still happening. It emphasizes the duration of an activity. For instance, “I have been studying for two hours.” This indicates ongoing action and time spent.
Use the Present Perfect Tense for specific actions completed in the past. Use the Present Perfect Continuous Tense for actions that started in the past and continue now.
| Tense | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Perfect | Completed actions | I have read the book. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Ongoing actions | I have been reading the book. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense describes actions that have occurred at an unspecified time. It connects past actions to the present. For example, “I have finished my homework. ” This tense emphasizes the result of the action rather than the action itself.
How Is Present Perfect Continuous Different?
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense focuses on the duration of an action that started in the past and continues into the present. For instance, “I have been studying for two hours. ” This tense highlights ongoing actions rather than completed ones.
Can You Give Examples Of Both Tenses?
Certainly! For Present Perfect, an example is “She has traveled to France. ” In contrast, an example of Present Perfect Continuous is “They have been playing soccer. ” Each tense provides different insights into the timing and nature of actions.
When Should I Use Each Tense?
Use Present Perfect for completed actions relevant to now. Choose Present Perfect Continuous when emphasizing ongoing actions or their duration. Understanding context is key to using these tenses correctly in your writing.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between the present perfect tense and the present perfect continuous tense is crucial for effective communication. Each tense serves a unique purpose in conveying time and action. By practicing with examples, you can improve your grammar skills and enhance your writing.
Master these tenses for clearer expression.
