The present simple tense describes habitual actions or general truths, while the present continuous tense indicates ongoing actions. For example, “She reads every morning” uses the present simple, whereas “She is reading right now” employs the present continuous.
Understanding verb tenses is crucial for effective communication in English. The present simple tense conveys routine activities, facts, and scheduled events. It often includes keywords like “always” and “usually. ” On the other hand, the present continuous tense highlights actions happening at this moment or temporary situations.
This tense frequently features words like “now” and “currently. ” Mastering these tenses enhances clarity in conversations and writing, allowing for more precise expression of time-related information. Both tenses play vital roles in everyday language use.
Introduction To Present Tenses
The Present Simple Tense describes habits and routines. It uses the base form of the verb. For example, “She reads every day.” This tense also shows facts. “The sun rises in the east.” It is straightforward and easy to understand.
The Present Continuous Tense shows actions happening now. It uses the verb “to be” plus the verb with an -ing ending. For example, “He is reading right now.” This tense can also describe future plans. “They are going to the park tomorrow.” It emphasizes ongoing actions.
Key Characteristics Of Present Simple Tense
The Present Simple Tense is used for general truths and facts. For example, “The sun rises in the east.” This tense shows things that are always true.
It also describes habits and routines. For instance, “She goes to school every day.” This indicates actions that happen regularly.
Another example is, “He drinks coffee in the morning.” This sentence shows a daily habit. Using the Present Simple makes communication clear and straightforward.
Key Characteristics Of Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense describes actions happening right now. For example, “She is running.” This shows the action is ongoing. It captures the current activity of the subject.
Temporary situations also use this tense. For instance, “He is living in Paris.” This indicates that his stay is not permanent. The focus is on the temporary nature of the situation.
Using the Present Continuous Tense helps to express actions in progress. It shows what someone is doing at this moment. These characteristics make it different from the Present Simple Tense.
Forming The Present Simple Tense
To form the Present Simple Tense, use the base form of the verb. For he, she, and it, add -s or -es. For example, “He plays soccer” or “She watches TV.” This tense shows habits or facts.
Verb Conjugation is important in the Present Simple. Here are some examples:
| Subject | Verb | Example |
|---|---|---|
| I/You/We/They | Base form | I play soccer. |
| He/She/It | Base form + -s/-es | She plays soccer. |
Common mistakes include using the wrong form of the verb. For instance, saying “He play soccer” is incorrect. Always remember to add -s for he, she, and it.
Forming The Present Continuous Tense
Forming the Present Continuous Tense involves using the verbs am, is, and are followed by the verb + ing.
Here’s how to use them:
| Subject | Verb Form |
|---|---|
| I | am eating |
| You | are playing |
| He/She/It | is running |
| We | are studying |
| They | are dancing |
Use am with I, is with he, she, or it, and are with you, we, or they.
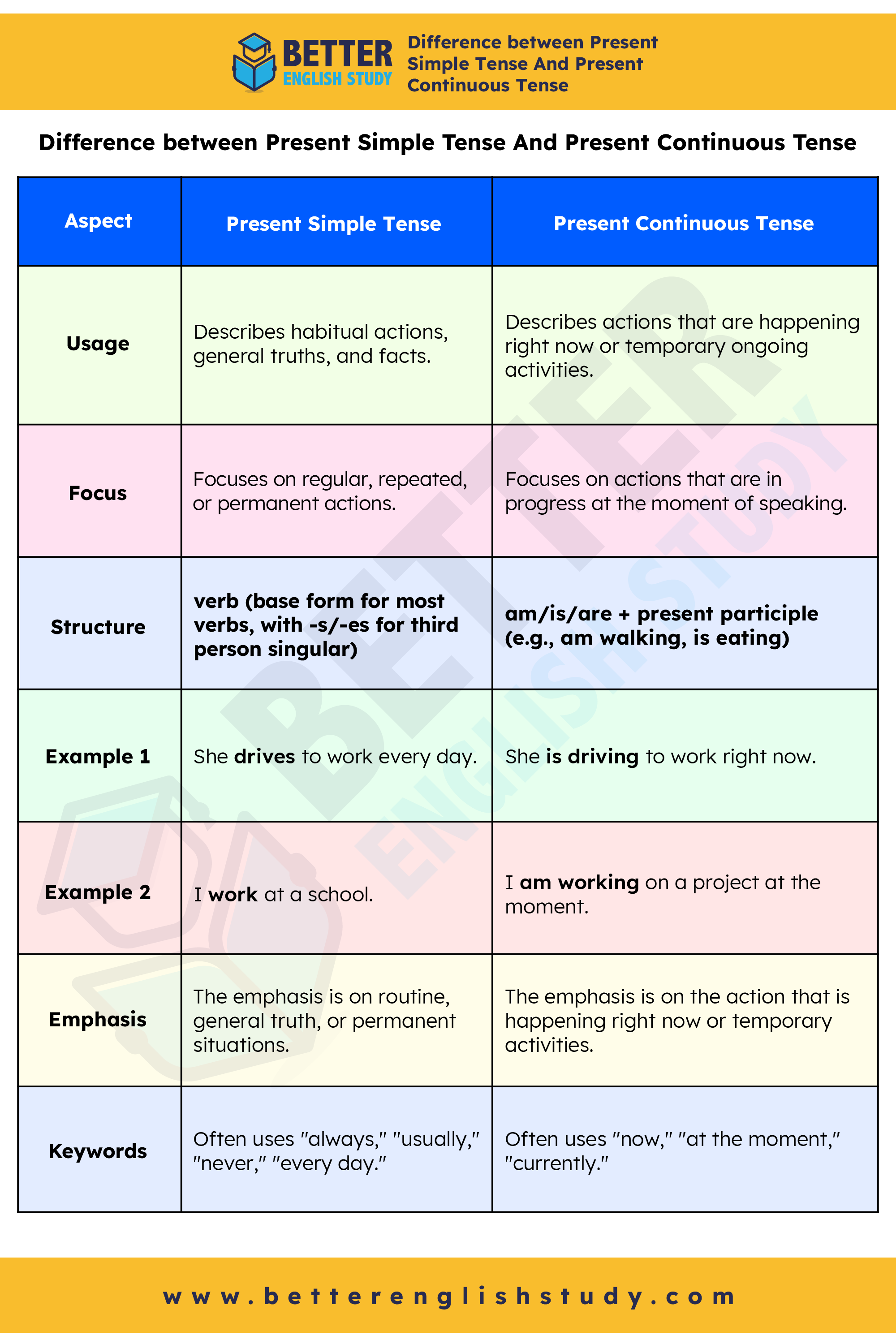
Difference between Present Simple Tense And Present Continuous
| Aspect | Present Simple Tense | Present Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes habitual actions, general truths, and facts. | Describes actions that are happening right now or temporary ongoing activities. |
| Focus | Focuses on regular, repeated, or permanent actions. | Focuses on actions that are in progress at the moment of speaking. |
| Structure | verb (base form for most verbs, with -s/-es for third person singular) | am/is/are + present participle (e.g., am walking, is eating) |
| Example 1 | She drives to work every day. | She is driving to work right now. |
| Example 2 | I work at a school. | I am working on a project at the moment. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on routine, general truth, or permanent situations. | The emphasis is on the action that is happening right now or temporary activities. |
| Keywords | Often uses “always,” “usually,” “never,” “every day.” | Often uses “now,” “at the moment,” “currently.” |
- Present simple describes habits, routines, facts, and things that are always or generally true.
- Present continuous describes actions happening at the moment of speaking or temporary ongoing situations.
Practical Applications
Using the present simple tense in academic writing helps to state facts. It shows general truths and regular actions. For example, “The Earth orbits the Sun.” This tense is clear and direct.
The present continuous tense describes ongoing actions. It is useful for explaining processes. An example is, “Researchers are studying climate change.” This tense adds a sense of immediacy.
In everyday conversation, the present simple tense is common for routines. For instance, “I go to school every day.” It communicates habits easily.
The present continuous tense is often used to discuss current activities. An example would be, “She is reading a book now.” This helps listeners understand what is happening right now.
Tips To Master Both Tenses
To master the Present Simple and Present Continuous tenses, practice is key. Use exercises that challenge you to identify the correct tense. For example, fill in the blanks with the right form of the verb.
Some effective practice exercises include:
- Complete sentences with the correct tense.
- Change sentences from Present Simple to Present Continuous.
- Identify the tense used in given sentences.
Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Confusing habitual actions with ongoing actions.
- Using the wrong form of the verb.
- Neglecting subject-verb agreement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Present Simple Tense Used For?
The present simple tense describes habitual actions or general truths. It is often used for routines, facts, and scheduled events. For example, “She reads every morning. ” This tense focuses on actions that are regular or permanent, highlighting a sense of stability in time.
How Does The Present Continuous Tense Function?
The present continuous tense indicates actions currently in progress. It is formed using “am,” “is,” or “are” with the verb’s -ing form. For example, “She is reading now. ” This tense emphasizes ongoing actions and dynamic situations, reflecting changes or developments in real-time.
Can You Provide Examples Of Both Tenses?
Certainly! For the present simple, an example is, “He plays soccer every Saturday. ” For the present continuous, an example is, “He is playing soccer right now. ” These examples illustrate the difference in focus between habitual actions and actions currently taking place.
What Are Common Mistakes With These Tenses?
Common mistakes include using the wrong tense for the situation. For instance, saying “I am going to school every day” instead of “I go to school every day. ” Understanding the context is crucial. This helps ensure accurate communication and proper tense usage in various scenarios.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between the present simple and present continuous tenses is crucial for effective communication. The present simple describes habits and facts, while the present continuous indicates ongoing actions. Mastering these tenses will enhance your writing and speaking skills, making your English more fluid and natural.
Keep practicing with examples for better retention.
