The Present Simple tense describes habitual actions or general truths, while the Present Perfect Continuous tense emphasizes ongoing actions that started in the past and continue to the present. For example, “She reads every morning” showcases a routine, whereas “She has been reading for two hours” highlights the duration of the activity.
Understanding verb tenses enhances your communication skills. Tenses indicate when actions take place, making your sentences clearer. The Present Simple tense often conveys routines and facts, making it essential for daily conversations. In contrast, the Present Perfect Continuous tense captures ongoing actions, focusing on their duration and relevance.
Both tenses serve unique purposes in effective communication, and mastering them is crucial for fluency.
Introduction To Present Tenses
The Present Simple Tense describes habits, routines, or facts. For example, “She walks to school.” This tense is often used with adverbs like always and never.
On the other hand, the Present Perfect Continuous Tense focuses on actions that started in the past and are still ongoing. An example is “He has been studying for two hours.” This tense shows duration and emphasizes continuity.
| Tense | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Habits, routines, facts | She plays soccer. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Actions still ongoing | They have been running. |
Forming Present Simple Tense
The Present Simple Tense is formed using the base form of the verb. For example, “I eat” or “She plays.” The structure is simple: Subject + Base Verb + (s/es for third person). This tense shows routine actions or facts.
Common uses of the Present Simple include describing daily habits, stating facts, and expressing general truths. For example:
- I play soccer every Saturday.
- The sun rises in the east.
- She likes chocolate.
Forming Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is formed using the verb “have,” “been,” and the -ing form of the main verb. For example, “I have been studying.” This shows an action that started in the past and continues now.
Common uses of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense include:
- To show actions that started in the past and are still happening.
- To emphasize the duration of an activity.
- To explain recent actions that have effects now.
Examples:
- She has been playing soccer for two hours.
- They have been waiting for the bus since morning.
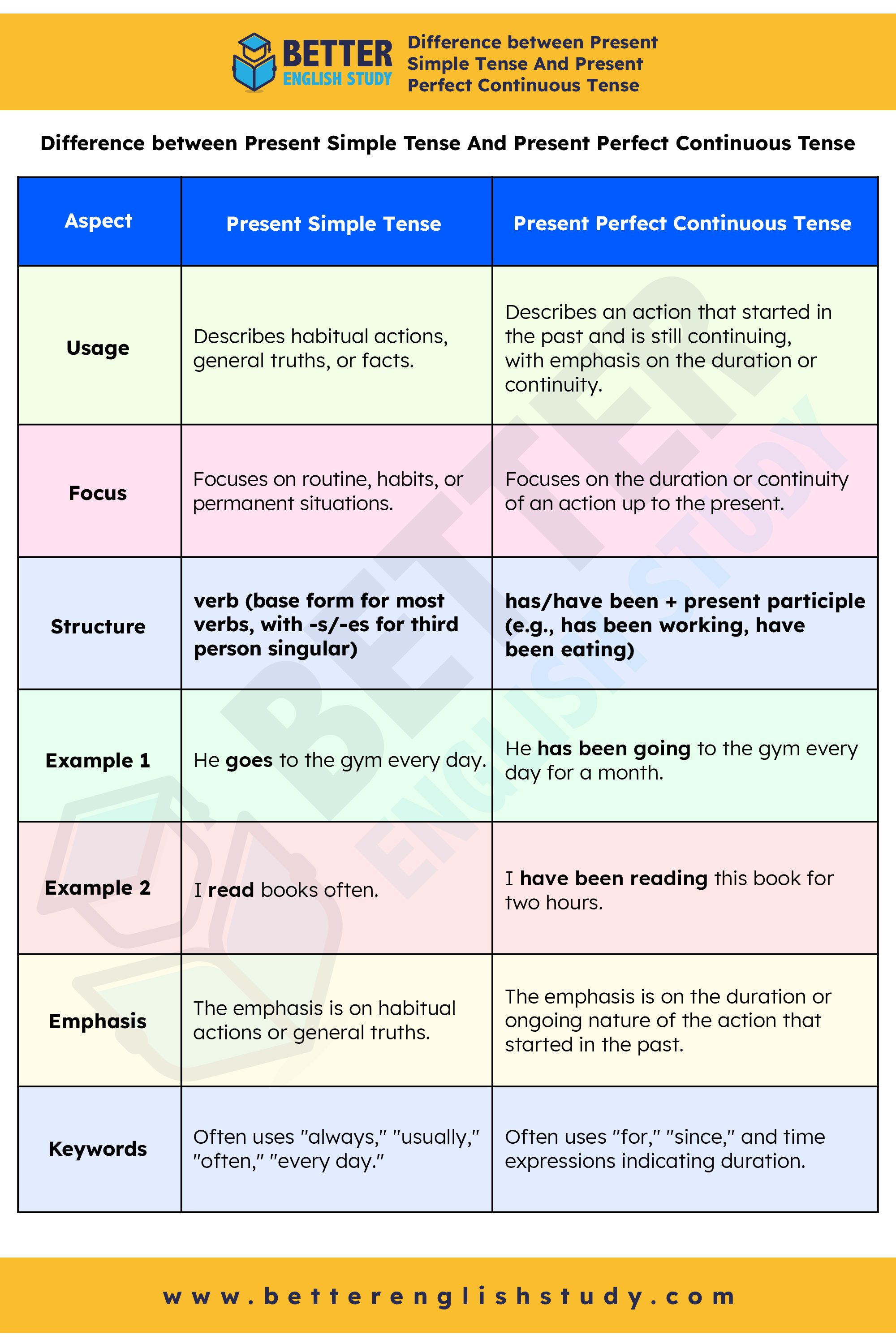
Difference between Present Simple Tense And Present Perfect Continuous Tense
| Aspect | Present Simple Tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes habitual actions, general truths, or facts. | Describes an action that started in the past and is still continuing, with emphasis on the duration or continuity. |
| Focus | Focuses on routine, habits, or permanent situations. | Focuses on the duration or continuity of an action up to the present. |
| Structure | verb (base form for most verbs, with -s/-es for third person singular) | has/have been + present participle (e.g., has been working, have been eating) |
| Example 1 | He goes to the gym every day. | He has been going to the gym every day for a month. |
| Example 2 | I read books often. | I have been reading this book for two hours. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on habitual actions or general truths. | The emphasis is on the duration or ongoing nature of the action that started in the past. |
| Keywords | Often uses “always,” “usually,” “often,” “every day.” | Often uses “for,” “since,” and time expressions indicating duration. |
- Present simple describes habits, routines, or facts that are generally true or regularly repeated.
- Present perfect continuous describes actions that began in the past and are still continuing, emphasizing how long the action has been going on.
Examples In Action
Present simple tense shows habits and routines. For example, “She plays soccer every weekend.” This tense describes actions that are regular and predictable.
Another example is, “He studies math after school.” This indicates a consistent action in daily life.
Present perfect continuous tense highlights ongoing actions. An example is, “They have been playing soccer for two hours.” This shows an action that started in the past and continues now.
Another example is, “She has been studying math since morning.” This emphasizes the duration of the activity.
Choosing The Right Tense
Choosing the right tense is important in English. Ask yourself these questions:
- What action is happening now?
- Is the action finished or ongoing?
- How long has the action been happening?
- Do I need to show a habit or routine?
Understanding these questions helps clarify tense usage.
For non-native speakers, practice is key. Use simple sentences to describe daily activities. Here are some tips:
- Write down your daily routine.
- Listen to native speakers.
- Practice speaking with friends.
- Read books in English.
These methods can improve your tense usage greatly.
Practice Exercises
Identifying tenses is essential in understanding grammar. The Present Simple Tense describes actions that happen regularly. For example, “She plays soccer.” The Present Perfect Continuous Tense shows actions that started in the past and are still happening. An example is, “She has been playing soccer.”
Converting sentences between tenses can be tricky. Here are some examples:
| Present Simple | Present Perfect Continuous |
|---|---|
| I read books. | I have been reading books. |
| They eat dinner. | They have been eating dinner. |
| He writes stories. | He has been writing stories. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Present Simple Tense?
The Present Simple Tense describes habitual actions or general truths. It is used for routines, facts, and permanent situations. For example, “She reads every morning” illustrates a regular action. This tense is straightforward and commonly used in daily conversations.
How Is Present Perfect Continuous Different?
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense focuses on actions that began in the past and continue to the present. It emphasizes the duration of an activity. For instance, “I have been reading for two hours” highlights ongoing action. This tense shows both past and present connections.
When To Use Present Simple?
Use Present Simple for regular actions and facts. It is ideal for schedules, habits, and universal truths. For example, “The sun rises in the east” states a fact. It’s essential for clear communication in everyday situations.
Can Present Perfect Continuous Show Completed Actions?
No, Present Perfect Continuous focuses on ongoing actions rather than completed ones. It highlights the duration and ongoing nature of activities. For example, “I have been studying” implies the action is still in progress. Completed actions use the Present Perfect tense instead.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between the present simple tense and the present perfect continuous tense is essential for effective communication. Each tense serves a unique purpose in expressing time and action. By practicing with examples, you can enhance your grasp of these tenses.
Mastering them will improve your writing and speaking skills significantly.
