The Present Simple tense describes habitual actions or general truths. The Present Perfect tense indicates actions that occurred at an unspecified time or that have relevance to the present.
Understanding verb tenses is crucial for effective communication in English. The Present Simple tense often highlights routines or facts, such as “She reads every day. ” In contrast, the Present Perfect tense connects past actions to the present, as in “She has read five books this month.”
Mastering these tenses can enhance clarity and precision in writing and speaking. Whether you’re crafting essays or engaging in conversations, knowing when to use each tense can make a significant difference. This knowledge not only improves grammar but also enriches your overall language skills.
Introduction To Present Tenses
The Present Simple Tense describes actions that happen regularly. For example, “She reads every day.” It shows habits and routines.
The Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present. For instance, “He has eaten lunch.” This tense focuses on the result of the action.
Understanding the significance of time is crucial in English grammar. The Present Simple emphasizes frequency, while the Present Perfect highlights completion.
Using these tenses correctly improves communication. It helps express thoughts clearly and accurately.
Diving Into Present Simple Tense
The Present Simple Tense is often used for regular actions. It describes habits, routines, and facts. For example, “She walks to school every day.” This sentence shows a daily routine.
Its structure is quite simple. You use the base form of the verb. For third-person singular, add -s or -es. For example, “He plays soccer.” In negative sentences, use “do not” or “does not.” Example: “They do not like broccoli.”
| Common Situations | Examples |
|---|---|
| Daily Routines | She brushes her teeth twice. |
| General Facts | The sun rises in the east. |
| Scheduled Events | The train leaves at 6 PM. |
Exploring Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense shows actions that happened at an unspecified time. It is formed using “have” or “has” with the past participle of a verb. For example, “She has eaten breakfast.” This tense connects the past with the present moment.
Typical scenarios for using the Present Perfect Tense include:
- To show experiences: “I have visited Paris.”
- To express changes: “He has grown taller.”
- To indicate achievements: “They have won a trophy.”
- To discuss recent events: “She has just finished her homework.”
This tense helps to focus on the result rather than the specific time of the action.
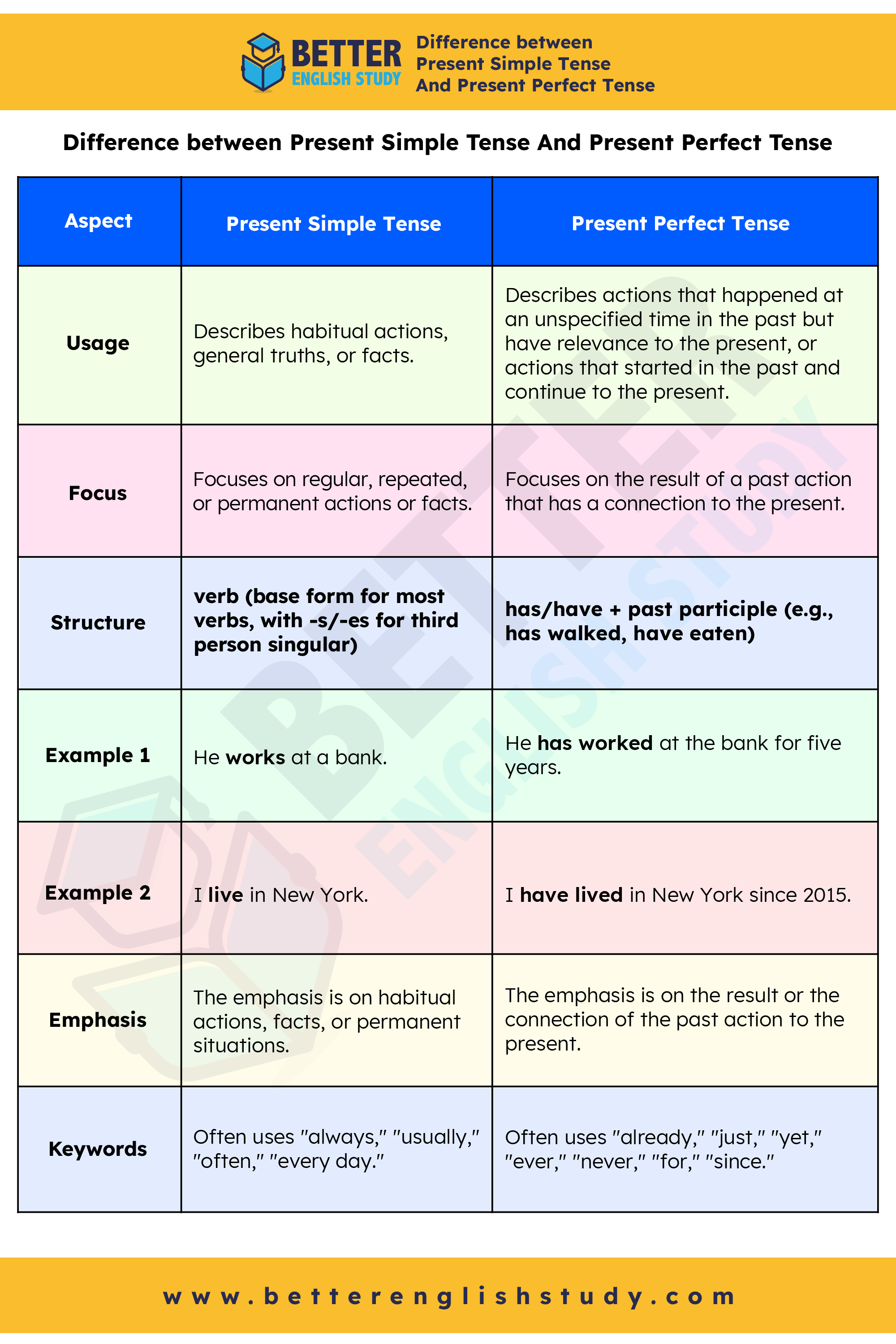
Difference between Present Simple Tense And Present Perfect Tense
| Aspect | Present Simple Tense | Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describes habitual actions, general truths, or facts. | Describes actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past but have relevance to the present, or actions that started in the past and continue to the present. |
| Focus | Focuses on regular, repeated, or permanent actions or facts. | Focuses on the result of a past action that has a connection to the present. |
| Structure | verb (base form for most verbs, with -s/-es for third person singular) | has/have + past participle (e.g., has walked, have eaten) |
| Example 1 | He works at a bank. | He has worked at the bank for five years. |
| Example 2 | I live in New York. | I have lived in New York since 2015. |
| Emphasis | The emphasis is on habitual actions, facts, or permanent situations. | The emphasis is on the result or the connection of the past action to the present. |
| Keywords | Often uses “always,” “usually,” “often,” “every day.” | Often uses “already,” “just,” “yet,” “ever,” “never,” “for,” “since.” |
- Present simple describes habitual actions, routines, general truths, or permanent situations.
- Present perfect describes actions that happened in the past but still have relevance to the present or actions that started in the past and continue into the present.
Verb Forms And Examples
The Present Simple Tense is used for actions that are regular or habitual. For example, “She reads books every day.” The structure is simple: subject + base form of the verb.
The Present Perfect Tense shows actions that happened at an unspecified time. For instance, “He has visited France.” Here, the structure is subject + has/have + past participle.
| Present Simple | Present Perfect |
|---|---|
| I play soccer. | I have played soccer. |
| She walks to school. | She has walked to school. |
| They eat lunch at noon. | They have eaten lunch. |
Time Expressions In Focus
Present Simple Tense often uses time indicators like always, usually, and every day. These words show regular actions. For example, “I eat breakfast at 7 AM.” This shows a habit.
Present Perfect Tense uses time indicators like already, ever, and just. These words show completed actions at some point. An example is “I have eaten breakfast.” This indicates an experience.
| Time Indicators | Present Simple | Present Perfect |
|---|---|---|
| Always | He always plays soccer. | – |
| Already | – | She has already finished her homework. |
| Usually | They usually go to school. | – |
| Ever | – | Have you ever been to Paris? |
Practical Applications
Understanding the Present Simple Tense and Present Perfect Tense helps in daily conversations. The Present Simple is used for routines and habits. For example, “I eat breakfast every day.” It describes actions that are true now.
The Present Perfect indicates actions that happened at an unspecified time. For instance, “I have eaten breakfast.” This shows a connection to the present.
| Context | Present Simple Example | Present Perfect Example |
|---|---|---|
| Everyday Language | I play soccer on weekends. | I have played soccer today. |
| Professional Contexts | The team meets every Monday. | The team has met several times this month. |
Common Mistakes To Avoid
A common mistake is mixing up tense usage. The present simple tense describes habits or facts. For example, “She reads books.” The present perfect tense indicates completed actions. For instance, “She has read three books.” Understanding these differences is crucial.
Another issue arises from misinterpreting time expressions. Words like “always” and “never” fit with the present simple. For example, “I always eat breakfast.” On the other hand, present perfect uses terms like “already” or “yet.” An example is “I have already eaten breakfast.” Recognizing these time markers helps avoid errors.
Quiz And Exercises
Test your knowledge of the Present Simple Tense and Present Perfect Tense. Choose the correct form:
- She ___ (eat/eaten) breakfast every day.
- They ___ (have/has) completed their homework.
- I ___ (play/played) soccer on weekends.
- We ___ (visit/visited) the museum last week.
Try these sentences. Fill in the blanks:
- He ___ (go/goes) to school every day.
- She ___ (has/have) seen that movie.
- They ___ (finish/finished) their project yesterday.
- We ___ (watch/watched) a show every Friday.
Answers:
| Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1 | goes |
| 2 | has |
| 3 | finished |
| 4 | watch |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Present Simple Tense Used For?
Present Simple Tense describes habitual actions, facts, and routines. It indicates what happens regularly or universally. For example, “She reads every morning. ” This tense is straightforward and emphasizes the consistency of actions over time.
How Is Present Perfect Tense Different?
Present Perfect Tense connects past actions to the present. It focuses on experiences or actions that have relevance now. For instance, “I have visited France. ” This tense highlights accomplishments without specifying when they occurred, making it distinct from the Present Simple.
Can You Give Examples Of Both Tenses?
Sure! An example of Present Simple is, “He plays football. ” For Present Perfect, you could say, “They have finished their homework. ” These examples illustrate the difference between regular actions and completed actions with current significance.
When Should I Use Each Tense?
Use Present Simple for routine actions and general truths. Opt for Present Perfect to discuss experiences or actions that affect the present. Knowing when to use each tense enhances clarity in communication and writing.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between the present simple tense and the present perfect tense is essential for clear communication. Each tense serves a unique purpose in expressing time and action. By practicing with examples, you can master these tenses and enhance your writing skills.
Keep exploring to become more confident in your grammar!
