Imagine you’re telling a friend about a movie you watched last night. You might say, “The actor who played the villain was fantastic.” That little word “who” is doing some heavy lifting here, connecting two ideas seamlessly.
This article dives into these crucial words, known as relative pronouns, which help our sentences flow and convey detailed information.
What Are Relative Pronouns in English?
Relative pronouns are words that introduce relative clauses, which are dependent (or relative) clauses that give more information about a noun in the sentence. They connect these clauses to an independent clause, creating a more detailed and cohesive statement.
For instance, in the sentence, “The book that you lent me was fascinating,” “that” is the relative pronoun linking the dependent clause “that you lent me” to the independent clause “The book was fascinating.”
Definition of Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are defined as pronouns that introduce relative clauses, which describe or provide more information about a noun. According to authoritative sources such as Merriam-Webster, a relative pronoun serves to introduce a clause that modifies a noun and typically refers to the noun directly preceding it.
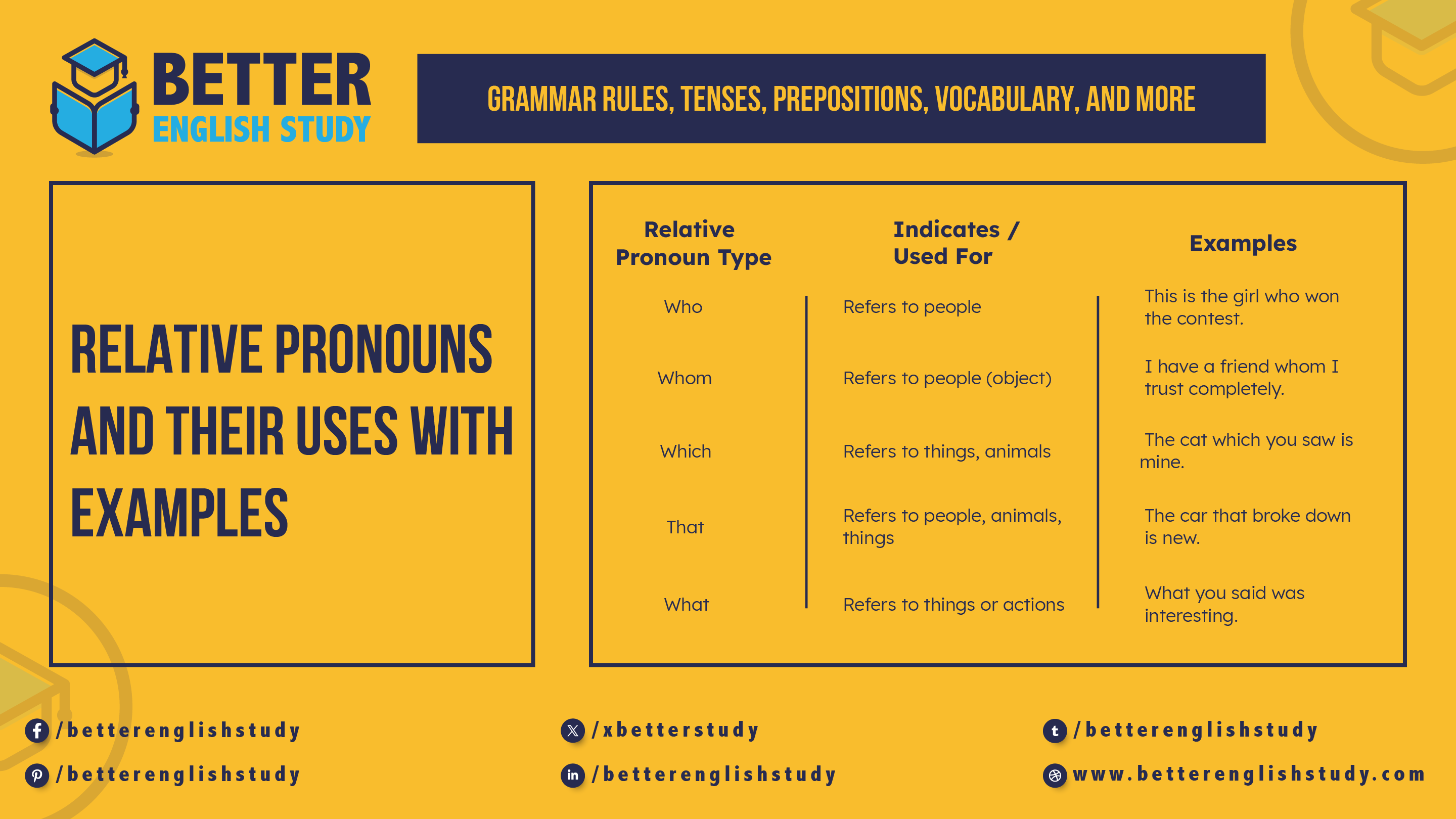
What Are the Relative Pronouns with Examples
1. Who
“Who” is used to refer to people and introduces a clause that describes someone.
Examples:
- The artist who painted this mural is famous.
- She’s the teacher who inspired me.
- I know the man who owns that car.
- Anyone who wants to join is welcome.
- The students who passed the exam are here.
- The doctor who treated me was very kind.
- This is the girl who won the contest.
- The person who called you is my friend.
- He’s the one who helped me with my project.
- The actor who starred in the movie is coming to town.
2. Whom
“Whom” is used to refer to people, particularly as the object of a verb or preposition.
Examples:
- The man whom you met yesterday is my uncle.
- She’s the author whom everyone admires.
- The people whom we invited are arriving soon.
- I have a friend whom I trust completely.
- The person to whom you spoke is my boss.
- The student whom the teacher praised is my brother.
- I know the person with whom you were talking.
- The woman whom they hired is very experienced.
- The person whom he thanked was surprised.
- She’s the one whom everyone likes.
3. Which
“Which” is used for things, animals, and sometimes to refer to a whole preceding clause.
Examples:
- The book which you lent me is fantastic.
- The house which we visited is beautiful.
- This is the movie which I was talking about.
- The cake which she baked was delicious.
- The cat which you saw is mine.
- The plan which they suggested seems good.
- The car which I bought is red.
- The gift which she received was unexpected.
- The project which he completed won an award.
- The painting which you admired is old.
4. That
“That” can refer to people, animals, or things and is often used in defining clauses.
Examples:
- The book that you gave me is amazing.
- The car that broke down is new.
- The man that we met is a lawyer.
- The cat that you saw is my pet.
- The house that was sold is on Elm Street.
- The project that we started is nearly finished.
- The song that you like is playing.
- The dog that barked is friendly.
- The student that won the prize is my cousin.
- The painting that was stolen has been found.
5. What
“What” refers to things or actions and introduces clauses that describe them.
Examples:
- I can’t believe what you did.
- Tell me what happened.
- What you said was interesting.
- I know what you mean.
- Do you remember what she told you?
- What he wrote was inspiring.
- What they offered was tempting.
- I wonder what he thinks.
- What she made was delicious.
- I’ll show you what I found.
Possessive Relative Pronouns
1. Whose
“Whose” indicates possession and can refer to people, animals, or things.
Examples:
- The boy whose bike was stolen is sad.
- The woman whose car broke down needs help.
- The artist whose painting won is here.
- The teacher whose class we enjoyed retired.
- The child whose toy was lost is crying.
- The author whose book I read is famous.
- The student whose grades improved is happy.
- The man whose wallet was found is relieved.
- The neighbor whose dog barked apologized.
- The person whose idea was chosen is excited.
Compound Relative Pronouns
Compound relative pronouns combine a pronoun with “ever” or “soever.”
1. Whatever
“Whatever” refers to anything or everything, without limitation.
Examples:
- Take whatever you want.
- Do whatever makes you happy.
- Choose whatever is best for you.
- I’ll support you in whatever you do.
- Whatever he decides is fine with me.
2. Whatsoever
“Whatsoever” is a more emphatic form of “whatever.”
Examples:
- There was no evidence whatsoever.
- I have no interest whatsoever.
- He showed no remorse whatsoever.
- She had no doubt whatsoever.
- They offered no help whatsoever.
3. Whoever
“Whoever” refers to any person or people, no matter who.
Examples:
- Whoever comes first will get a prize.
- Call whoever you want.
- Whoever finishes first wins.
- I’ll help whoever needs it.
- Whoever knows the answer should speak up.
4. Whosoever
“Whosoever” is an emphatic form of “whoever.”
Examples:
- Whosoever believes will be saved.
- Whosoever wants to join may come.
- Whosoever can answer should raise their hand.
- The prize goes to whosoever wins the race.
- Whosoever needs help can ask me.
5. Whichever
“Whichever” refers to any one or more from a known set.
Examples:
- Choose whichever book you like.
- Take whichever path you prefer.
- You can pick whichever you want.
- Whichever choice you make, I’ll support you.
- Whichever option is cheaper, let’s go with that.
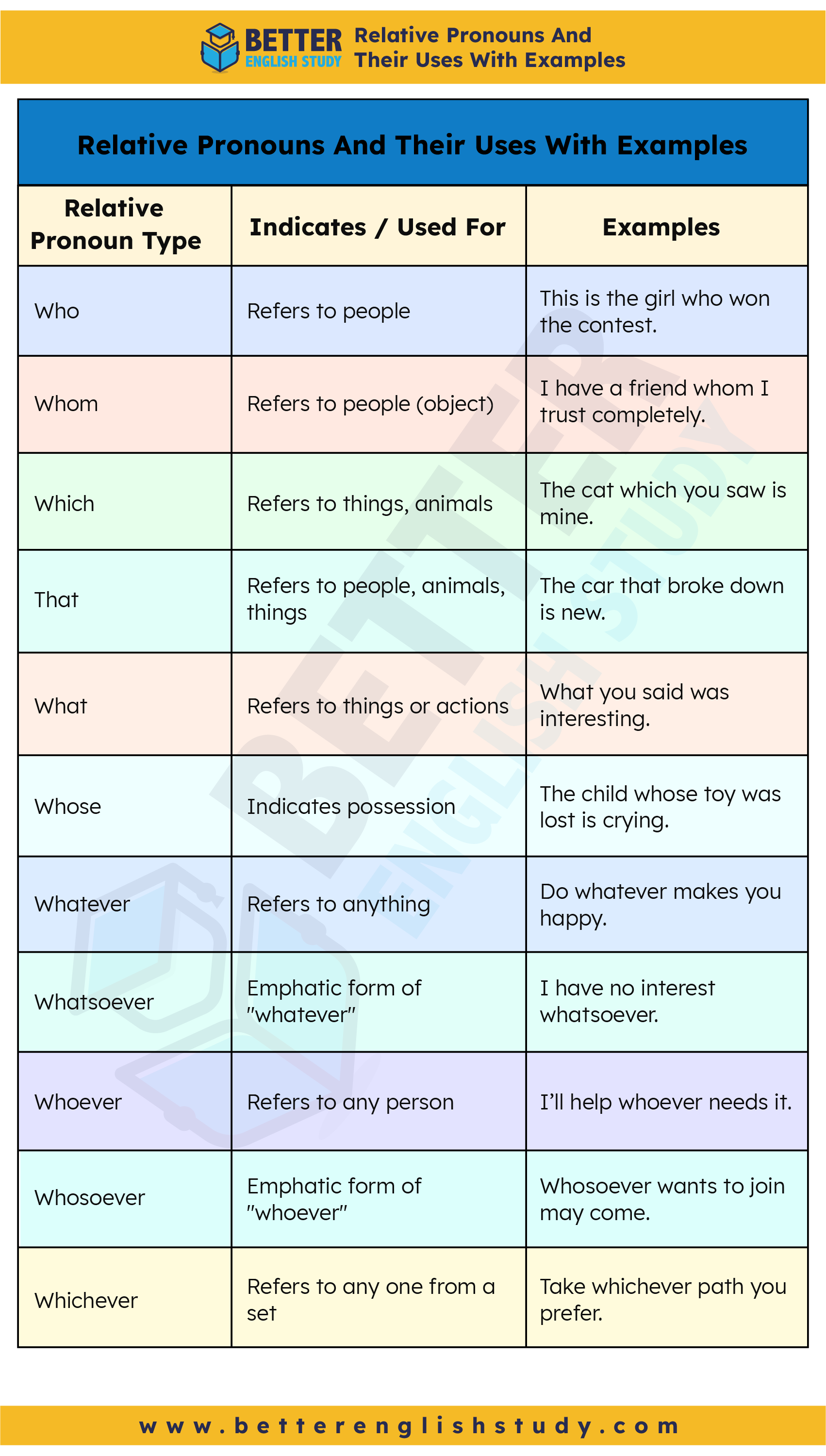
Summary Table of Relative Pronouns And Their Uses With Examples
| Relative Pronoun Type | Indicates / Used For | Examples |
| Who | Refers to people | This is the girl who won the contest. |
| Whom | Refers to people (object) | I have a friend whom I trust completely. |
| Which | Refers to things, animals | The cat which you saw is mine. |
| That | Refers to people, animals, things | The car that broke down is new. |
| What | Refers to things or actions | What you said was interesting. |
| Whose | Indicates possession | The child whose toy was lost is crying. |
| Whatever | Refers to anything | Do whatever makes you happy. |
| Whatsoever | Emphatic form of “whatever” | I have no interest whatsoever. |
| Whoever | Refers to any person | I’ll help whoever needs it. |
| Whosoever | Emphatic form of “whoever” | Whosoever wants to join may come. |
| Whichever | Refers to any one from a set | Take whichever path you prefer. |
Relative pronouns play a crucial role in English grammar by connecting dependent clauses to independent clauses, forming adjective clauses that provide additional information about nouns. Whether referring to people, places, things, animals, or ideas, these pronouns make our sentences richer and more detailed, enabling us to communicate with greater clarity and precision.
